

做过的题你都能拿分吗?

临近考试,小编相信大家都开始启用“题海”战术,疯狂刷题,可是你现在做过的题,你考场碰到都能做对吗?
同为备考党的我,小编只想说,如果只做过一遍,那怕是有点难。

我相信大家都是从题海战术里走出来的朋友们,这其实就是一个熟能生巧的事情,即时可能你对某个知识点不理解,但是同一个题型你做完3次后,就有一种闭着眼睛我都能认出你的熟悉感,剥掉题干的外壳,其实都是同一个套路。
那么到底哪些题目是有典型考法的,哪些知识点是比较易错的点,这就是大家考前需要拿个小本本记下来的事情。
看到这里,是不是大家都有一种蠢蠢欲动,要赶紧去做笔记的想法?

知道目前大家都在争分多秒学习,贴心的品职教研组的小哥哥、小姐姐们也是熬夜赶工(心疼一下),帮大家整理了CFA三个级别学科的错题本,希望在最后的时候能给大家起到助力的作用。
在接下来的几周里,我们会陆续发放三个级别的高频问答,希望对大家的备考有所帮助。今天二级放上衍生品的错题本,大家一起来看看这些题都会做吗?


forward求value的两种方法
题干
二级衍生大家疑惑比较多的就是forwad 合约求value的两种方法的应用。所以我先在开始给大家讲下这两个方法和原理:对于forward 合约求value,有两种做法。
![]() 第一种方法:
第一种方法:
就是已知或先计算出当前市场上的forward price,即Ft(T),然后与0时刻我们签订合约的F0(T)轧差,再折现至t时刻。对于longposition,Vt(T) = PVt,T[Ft(T) – F0(T)]。

比如说我3月1号签了一个合约,约定5月1号花5块钱买一个苹果,这里的5块钱就是F0(T)。在4月25号,我想看下我签这个合约是赚是亏,那我就可以在市场上签一个反向对冲合约,也就是签订一个5月1号卖一个苹果的合约,合约约定的卖苹果价格就是Ft(T),这样就相当于我在今天就把原来签的合约平仓平掉了,原来签的合约赚多少亏多少我今天就确定了。
那原来签署这份合约带给我的价值就等于:今天我签署的对冲合约,也就是5月1号卖苹果收到的钱-我3月1号签署合约约定的5月1号买苹果付出的钱,也就是Ft(T)- F0(T)再折现到4月25号。折现是因为现金流是发生在5月1号,需要折现到t时刻也就是4月28号才是t时刻的value。
![]() 第二种方法:
第二种方法:
就是,t时刻,value =收到的现金流减去支出的现金流。假设期间没有其它持有成本和额外收益。
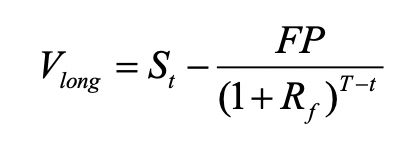
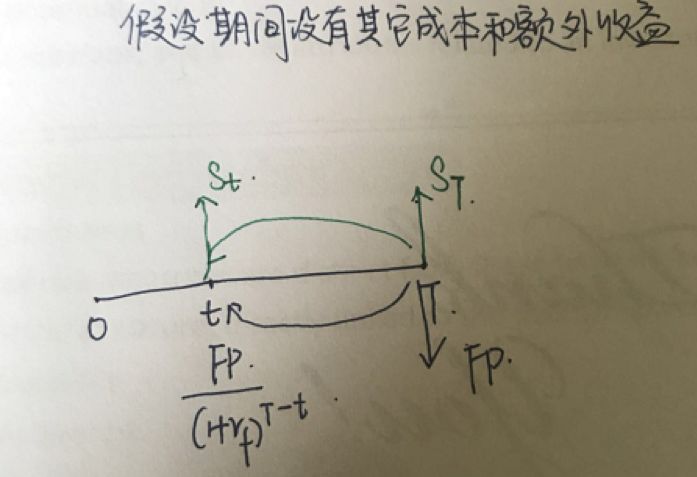
做题和考试的时候,如果题目给了Ft(T),就优先用第一种方法算,如果没给,就优先用第二种方法算。
接下来我们看下大家疑问比较多的题目。

精选问答1
题干
Troubadour takes a short position in the TSI equity forward contract. His supervisorasks, “Under which scenario would our position experience a loss?”
The most appropriate response to Troubadour’s supervisor’s questionregarding the TSI forward contract is:
A.a decrease in TSI’s share price, all else equal.
B.an increase in the risk-free rate, all else equal.
C.a decrease in the market price of the forward contract, all else equal.
答案解析
B is correct.
From the perspective of the long position, the forward value is equal to the present value of the difference in forward prices:
Vt(T)= PVt,T[Ft(T)-F0(T)]
where Ft(T) =FVt,T(St+θt-γt)
All else equal, an increase in the risk-free rate before contract expiration would cause the forward price, Ft(T), to increase.
This increase in theforward price would cause the value of the TSI forward contract, from the perspective of the short, to decrease.
Therefore, an increase in the risk-free rate would lead to a loss on the short position in the TSI forward contract.
解题思路
这道题是说在哪种情况下,签订equity forward contract的short方有一个亏损。对于A、B选项,我们可以直接根据这个公式判断:假设股票不分红,对于short 方来说Vt=F/(1+r)T-t-St。
![]() A选项:a decrease in TSI’s share price, all else equal, St下跌,Vt增加,short 方赚钱。A选项不对。
A选项:a decrease in TSI’s share price, all else equal, St下跌,Vt增加,short 方赚钱。A选项不对。
![]() B选项:an increase in the risk-free rate, all else equal。无风险利率上升,F/(1+r)T-t分母增大,整个式子减小,所以short方亏钱。B选项正确。
B选项:an increase in the risk-free rate, all else equal。无风险利率上升,F/(1+r)T-t分母增大,整个式子减小,所以short方亏钱。B选项正确。
![]() C选项: a decrease in the market price of the forward contract, all else equal. 当前市场上forward contract的价格下跌,说明如果我在当前市场上签订合约约定T时刻卖股票的价格小于0时刻我签定合约约定T时刻卖股票的价格,那么说明我原本签订的这份合约是赚钱的。C选项错误。
C选项: a decrease in the market price of the forward contract, all else equal. 当前市场上forward contract的价格下跌,说明如果我在当前市场上签订合约约定T时刻卖股票的价格小于0时刻我签定合约约定T时刻卖股票的价格,那么说明我原本签订的这份合约是赚钱的。C选项错误。
或者也可以直接根据公式Vt(T) = PVt,T[Ft(T)– F0(T)] ,这里的Ft(T)是指t时刻签订forword contract约定的T时刻买股票的价格,而F0(T)是指0时刻签订合约时约定的T时刻买股票的价格。题目中说market price of forwardcontract 减少,即Ft(T)减少,此时long position亏钱,short position 则赚钱。C选项错误。
易错点分析
这道题目A、B选项对大家来说判断都比较容易,但是C选项就不容易理解。主要是大家不知道the market price of the forward contract是什么意思。
the market price of the forward contract是指t时刻签订一份forward contract约定的forward price,即Ft(T)。对于Fx(),下标x表示的是签订合约的时间,括号里面的字母表示合约的到期日。

精选问答2
题干
Johnson reviews a 6 x 9 FRA that the bank entered into 90 days ago as the pay-fixed/ receive-floating party. Selected data for the FRA are presented in Exhibit 6, and current Libor data are presented in Exhibit 7.
Based on her interest rate forecast, Johnson also considers whether the bank should enter into new positions in 1 x 4 and 2 x 5 FRAs.
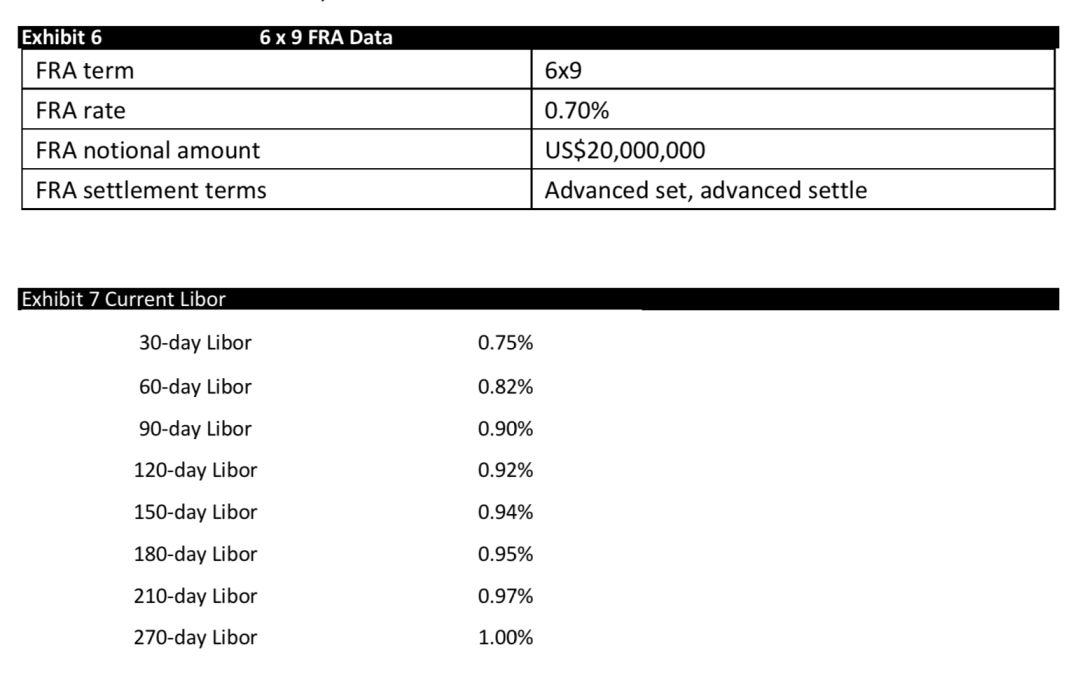
Three months later, the 6 x 9 FRA in Exhibit 6 reaches expiration, at which time the three-month US dollar Libor is1.10% and the six-month US dollar Libor is 1.20%. Johnson determines that the appropriate discount rate for the FRA settlement cash flows is 1.10%.
From the bank’s perspective, based on Exhibits 6 and 7,the value of the 6 x 9 FRA 90 days after inception is closest to:
$14,817.
$19,647.
$29,635.
答案解析
A is correct.
The current value of the 6 x 9 FRAis calculated as
Vg(0,h,m) ={[FRA(g,h - g,m) - FRA(0,h,m)]tm}/[1 + Dg(h+ m - g)th+m-g]
The 6 x 9 FRA expires six months after initiation. The bank entered into the FRA 90 days ago; thus, the FRA willexpire in 90 days.
To value the FRA, the first step is to compute the new FRA rate, which is the rate on Day 90 of an FRA that expires in 90 days in which the underlying is the 90-day Libor, or FRA(90,90,90):
FRA(g,h -g,m) = {[1 + Lg(h - g + m)th-g+m]/[1 +L0(h - g)th-g] - 1}/tm
FRA(90,90,90)= {[1 + L90(180 - 90 + 90)(180/360)]/[1 + L90(180 - 90)(90/360)] - 1}/(90/360)
FRA(90,90,90)= {[1 + L90(180)(180/360)]/[1 + L90(90)(90/360)] - 1}/(90/360)
Exhibit 7indicates that L90(180) = 0.95% and L90(90) = 0.90%, so
FRA(90,90,90)= {[1 + 0.0095(180/360)]/[1 + 0.0090(90/360)] - 1}/(90/360)
FRA(90,90,90)= [(1.00475/1.00225) - 1](4) = 0.009978, or 0.9978%
Therefore,given the FRA rate at initiation of 0.70% and notional principal of $20 million from Exhibit 1, the current value of the forward contract is calculated as
Vg(0,h,m) = V90(0,180,90)
V90(0,180,90) = $20,000,000[(0.009978- 0.0070)(90/360)]/[1 + 0.0095(180/360)].
V90(0,180,90) =$14,887.75/1.00475 = $14,817.37.
解题思路
这道题目是FRA求value。答案的做法是采用了第一种方法,先求出来当前市场上no arbitrage 的FRA rate,这个求法就和0时刻求FRA定价是一样的,FRA定价咱们基础班视频Interest Rate Forward andFutures 这节课有详细讲解,然后再与0时刻签订合约约定的FRA rate轧差,再折现。
相当于0时刻,我签定FRA约定未来的贷款利率是0.7%,T时刻支付的利息就是NP×0.0070×(90/360),而当前市场上的FRA rate是0. 9978%,说明我们0时刻签的合约是合算的。此时如果签订反向对冲合约平仓的话,T时刻我们就收到NP×0.009978×(90/360)这么多利息,支出NP×0.0070×(90/360)。Value就是二者之差再折现至t时刻。
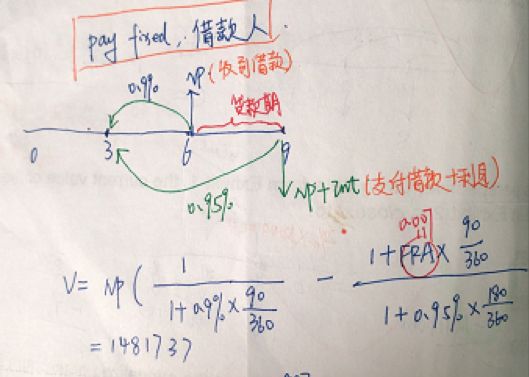
由于这道题没有给出当前市场上的FRA rate,我们也可以通过第二种做法做,画图计算过程如下:
易错点分析
![]() 这道题同学们一个疑惑的点就是不清楚bank的头寸,这里题目说bank entered into 90 daysago as the pay-fixed/ receive-floating party. pay-fixed/ receive-floating,支固定收浮动那么就是利率上升的时候赚钱,那就说明bank 是long FRA的一方。
这道题同学们一个疑惑的点就是不清楚bank的头寸,这里题目说bank entered into 90 daysago as the pay-fixed/ receive-floating party. pay-fixed/ receive-floating,支固定收浮动那么就是利率上升的时候赚钱,那就说明bank 是long FRA的一方。
![]() 第二个疑惑点,不知道6×9 FRA种的6和9分别代表什么,6代表FRA到期的时刻,也就是贷款开始的时刻,因为在贷款开始的时候,贷款利率就决定了,FRA也就可以到期结算了。
第二个疑惑点,不知道6×9 FRA种的6和9分别代表什么,6代表FRA到期的时刻,也就是贷款开始的时刻,因为在贷款开始的时候,贷款利率就决定了,FRA也就可以到期结算了。
![]() 第三个疑问就是不知道时间轴怎么画,时间点如何确定。J同学90天前进入6×9 FRA合约,如果我们画时间轴的时候把90天前画为0时刻,那么现在就是3时刻,6时刻是FRA到期,贷款开始,9时刻贷款结束。
第三个疑问就是不知道时间轴怎么画,时间点如何确定。J同学90天前进入6×9 FRA合约,如果我们画时间轴的时候把90天前画为0时刻,那么现在就是3时刻,6时刻是FRA到期,贷款开始,9时刻贷款结束。
![]() 第四个疑问就是折现利率的挑选,本金是往前折现3个月,那就要选择当前时刻三个月期限的贷款利率,本金+利息是往前折现6个月,那就要选择当前时刻六个月期限的贷款利率。
第四个疑问就是折现利率的挑选,本金是往前折现3个月,那就要选择当前时刻三个月期限的贷款利率,本金+利息是往前折现6个月,那就要选择当前时刻六个月期限的贷款利率。
![]() 最后一个疑问就是计算利息的时候去年化的问题。因为一般我们条件给出的都是年化的利率,我们在计算的时候需要折算成对应天数的利息。比如3个月的年化利率是0.9%,那么本金×0.9%相当于是1年的利息,再除以360相当于是1天的利息,再乘以对应的天数90天就是90天的利息。
最后一个疑问就是计算利息的时候去年化的问题。因为一般我们条件给出的都是年化的利率,我们在计算的时候需要折算成对应天数的利息。比如3个月的年化利率是0.9%,那么本金×0.9%相当于是1年的利息,再除以360相当于是1天的利息,再乘以对应的天数90天就是90天的利息。

精选问答3
题干
Based on Exhibit 6 and the three-month US dollar Libor at expiration, the payment amount that the bankwill receive to settle the 6 x 9 FRA is closest to:
A. $19,945.
B. $24,925.
C. $39,781.
答案解析
Given a three-month US dollar Libor of 1.10% at expiration, the settlement amount for the bank as the receive-floating party is calculated as
Settlement amount (receive floating) = NA{[Lh(m) -FRA(0,h,m)]tm}/[1 + Dh(m)tm]
Settlement amount (receive floating) = $20,000,000[(0.011 -0.0070)(90/360)]/[1 + 0.011(90/360)]
Settlement amount (receive floating) = $20,000/1.00275 = $19,945.15
Therefore, the bank will receive $19,945 (rounded) as thereceive-floating party.
解题思路
这道题目是典型的FRA求交割金额。对于FRA求交割金额,我们只有一种做法,以long 方为例,就是用(libor-FRA)去年化×NP,再折现至FRA到期日,也就是贷款开始日,相当于如果不签订合约,我的贷款利率是libor,签订合约后我的贷款利率是FRA约定的fix rate;那么交割的金额就是签订这份合约带给我的好处。
具体原理我们基础班视频第39章interest rate forward and futures:example这节课第4分钟(1.5倍速)有介绍。或者也可以理解为,bank entered pay-fixed支付的是固定利率是FRA rate, receive-floating收到的浮动利率是Libor。
而利息是发生在贷款到期日,而交割是发生在FRA到期日。那交割金额就是二者之差折现到FRA到期日。计算就是:Settlement amount =20,000,000[(0.011- 0.0070)(90/360)]/[1 + 0.011(90/360)] = $20,000/1.00275 = $19,945.15。
易错点分析
这道题同学们一个疑惑的点就是不清楚bank的头寸,这个区分我在上一个题目里面有说;第二个疑惑点就是不知道settlement日期是什么时候,对于FRA合约来说,在FRA合约到期的时候,也就是贷款开始的时候,进行交割。
第三个同学们不清楚的地方就是advanced set、advanced settled是什么意思。advanced set是说我们的存、贷款利率在存款或者贷款开始的时候就决定了。对3×6的FRA,那就是FRA到期的3时刻,贷款的利率就定下来了。
advanced settled是指我们签订这份FRA合约最终的结算是在贷款开始的时候也就是FRA到期的时刻结算,也就是3时刻结算,也就是3时刻我们就对这份合约进行交割。这个概念老师在基础班视频第39章interest rate forward and futures第13分钟(1.5倍速)有介绍。

精选问答4
题干
A dealer entered into a three-year interest rate swap with annual payments one year ago as a floating receiver. The current equilibrium fixed swap rate is 1.4853% (one year after the swap was originally entered).
The initial swap rateis 1.82% and notional principle is $100 million. The value of this swap is:
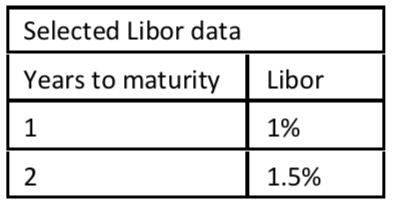
-690,598
656,338
-656,338
答案解析
C is correct.
Present Value Factor 1 = 1+1%× 360 360 =0.990099
Present Value Factor 2 = 1+1.5%× 720 360 =0.970874
投资者之前的合约是收浮动,付固定,现在进入反向合约,即收固定,付浮动。浮动端可以抵消,剩下的就是收新的固定利率,付之前合约中约定的swap rate。
向上箭头: current equilibrium fixed swap rate ,也就是以现在的市场条件签订一个到期日相同的合约的swap rate,它等于1.4853%。而且我们注意到,这是一个均衡的swap rate。Swap rate即固定利率,它可以看成是市场中浮动利率的打包价。所谓均衡就是说是无套利情况下计算出来的固定利率,即与interest swaprate的定价是一样的,就算题目没有告诉我们currentequilibrium fixed swap rate,我们也能计算:
1−0.970874 0.990099+0.970874 =1.4853%
每一期的差额=1.4853%-1.82%(最后一期的本金相互抵消),然后向前折现,折现因子已经求出,分别为0.990099和0.970874,所以:(1.4853%-1.82%)×(0.990099+0.970874)×100,000,000=−656,338 。
解题思路
因为这道题答案中已经给出了第一种计算方法的解题思路及过程,这种计算思路和方法我们基础班视频第39章Valuing Interest Rate Swap这节课第三分钟(1.5倍速)开始的例题讲解中有介绍。
我在这里主要写下第二种方法的解题思路:
易错点分析
![]() 这道题同学们有疑问的第一个点是不理解current equilibrium fixed swap rate是指什么。current equilibrium fixed swap rate是指在当前时刻,签署一份swap ,约定的swap rate ,在这道题中是1.4853%。
这道题同学们有疑问的第一个点是不理解current equilibrium fixed swap rate是指什么。current equilibrium fixed swap rate是指在当前时刻,签署一份swap ,约定的swap rate ,在这道题中是1.4853%。
那作为收浮动支固定的一方来说,如果按照当前市场上合约约定的swap rate,我们支出的固定利率就是1.4853%。但是由于我们0时刻签订了合约,约定的swap rate是1.82%,也就是说我们现在依然需要按照1.82%来支利息。
那站在现在时间点,我们签合约就是有亏损的的,亏损就是每一期必须多支出1.82%-1.4853%,再乘以本金折现就是签署这份合约的亏损。还有一个理解角度就是,当前时刻,签署一份swap ,约定的swap rate 是1.4853%。
那我就可以在当前市场上签署一份反向合约,把我原来的合约平仓平掉。原来是支固定1.82%,收浮动,那我现在就签一份收固定,支浮动的合约,两份合约结合起来就是支浮动、收浮动,支固定1.82%,收固定1.4853%。我的收益就是每一期收固定1.4853%-支固定1.82%,再乘以本金再折现就是现在的收益。
![]() 第二个疑问就是为什么说swap rate 是浮动利率的打包价。因为swap rate 是我们签订的利率互换合约中用来交换浮动利率的,相当于是买浮动利率的一个价格,只不过这个价格是固定利率。
第二个疑问就是为什么说swap rate 是浮动利率的打包价。因为swap rate 是我们签订的利率互换合约中用来交换浮动利率的,相当于是买浮动利率的一个价格,只不过这个价格是固定利率。
所以这道题我们可以理解为我们签订合约约定买浮动利率的价格是1.82%,但是现在市场上买浮动利率的价格是1.4853%。
![]() 第三个疑问就是为什么两种方法计算出来的结果很接近但是不相等,这个主要是因为题目给出的current equilibrium fixed swap rate =1.4853%也是四舍五入后的近似值,并非精确的equilibrium fixed swaprate,只有是精确的equilibrium fixed swaprate,二者的计算结果是一样的。所以说如果考试给出了当前市场上的equilibrium fixed swap rate,那就优先用这道题目答案中的方法计算。
第三个疑问就是为什么两种方法计算出来的结果很接近但是不相等,这个主要是因为题目给出的current equilibrium fixed swap rate =1.4853%也是四舍五入后的近似值,并非精确的equilibrium fixed swaprate,只有是精确的equilibrium fixed swaprate,二者的计算结果是一样的。所以说如果考试给出了当前市场上的equilibrium fixed swap rate,那就优先用这道题目答案中的方法计算。

精选问答5
题干
Troubadour identifies an arbitrage opportunity relating to a fixed-income futures contract and its underlying bond. Current data on the futures contract and underlying bond are presented in Exhibit 1. The current annual compounded risk-free rate is 0.30%.
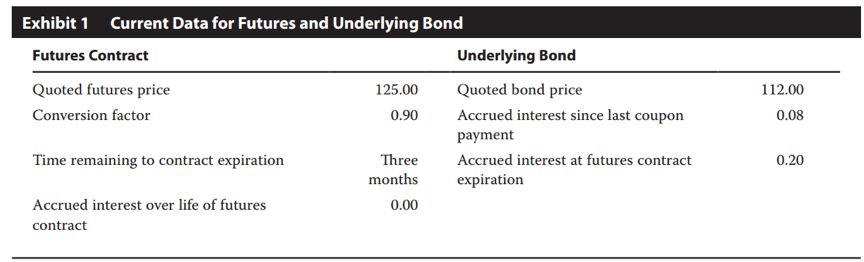
Based on Exhibit 1 and assuming annual compounding, the arbitrage profit on the bondfutures contract is closest to:
0.4518
0.5356
0.6195
答案解析
选B.
The no-arbitrage futures price is equal to the following:
F0(T) =FV0,T(T)[B0(T + Y) +Al0– PVCI0,T]
F0(T)= (1 + 0.003)0.25(112.00 + 0.08 -0)
F0(T) = (1 + 0.003)0.25 (112.08) = 112.1640
The adjusted price of the futures contract is equal to the conversion factor multiplied by the quoted futures price:
F0(T)=CF(T)QF0(T)
F0(T) = (0.90)(125) = 112.50
Adding the accrued interest of 0.20 in three month (futures contractexpiration) to the adjusted price of the futures contract gives a total priceof 112.70.
This difference means that the futures contract is overpriced by 112.70- 112.1640 = 0.5360. The available arbitrage profit is the present value of this difference: 0.5360/(1.003)0.25= 0.5356.
解题思路
如果市场上定价与我们计算的no arbitrage price 不同,那我们就可以进行套利。套利利润就是二者之差。
![]() 所以第一步就是计算no arbitrage futures price。这里要注意的就是对于债券来说,债券的报价是不含应计利息的clean price,实际我们买卖债券的时候支付的金额是债券的报价再加上accrued interest。
所以第一步就是计算no arbitrage futures price。这里要注意的就是对于债券来说,债券的报价是不含应计利息的clean price,实际我们买卖债券的时候支付的金额是债券的报价再加上accrued interest。
no arbitrage futures price,计算过程如下,其中B0表示0时刻债券的报价,AI0表示0时刻债券的accrued interest,AIT表示T时刻债券的accrued interest,(注意这里计算出来的FP也是futures的报价):

![]() 第二步:比较计算的no arbitrage 的FP和市场上的FP的价格。市场上的FP的价格= quoted futures price×conversion factor=(0.90)(125) = 112.50。
第二步:比较计算的no arbitrage 的FP和市场上的FP的价格。市场上的FP的价格= quoted futures price×conversion factor=(0.90)(125) = 112.50。
由于市场上的FP价格大于no arbitrage 的FP,那我们就可以买入定价低的卖出定价高的进行套利,套利利润就是(112.5+0.08)- (111.964+0.08)=0.536。
具体套利过程就是先借钱在现货市场上买入债券,然后签订一个futures合约,约定未来卖掉bond。期初买入bond 我们产生的现金流是:-(bond的价格+应计利息), futures 到期我们卖bond收到125*0.9+AIT。bond的价格是(112+0.08),加上利息就是(112+0.08)×1.0030.25=112.164;到期根据futures 卖出bond 我们是收到125*0.9+0.2=112.7总的利润就是112.7-112.164=0.536。
易错点分析
这道题同学们一个疑惑的点就是不清楚债券的报价是clean price,实际成交价是报价+accrued interest;另外一个疑惑的点是为什么0时刻还会有accrued interest,这里的0时刻是我们签订futures合约的时刻,并不是债券发行的时刻。
只要这个时间点不是债券的coupon day,就会有accrued interest产生。还有一个大家有疑问的就是conversion factor是作用在哪:conversion factor是和futures的报价相乘,得到具体对应标的债券futures的报价。相关的知识点在咱们基础班视频第39章fixed-income forward and futures这节课有介绍。

精选问答6
题干
Troubadour holds a short position in a yen/US dollar forward contractwith a notional value of $1,000,000. At contract initiation, the forward rate was ¥112.10 per $1. The forward contract expires in three months. The currentspot exchangerate is ¥112.00 per $1, and the annually compounded riskfree ratesare -0.20% for the yen and 0.30% for the US dollar. The current quoted price ofthe forward contract is equal to the no-arbitrage price.
The value of Position 3 is closest to:
A. -¥40,020.
B. ¥139,913.
C. ¥239,963.
答案解析
C is correct.
The current no-arbitrage price of the forward contract is
Ft(¥/$,T) = St(¥/$)FV¥,t,T(1)/FV$,t,T(1)
Ft(¥/$,T) = ¥112.00(1 - 0.002)0.25/(1 +0.003)0.25 = ¥111.8602
Therefore, the value of Troubadour’s position inthe ¥/$ forward contract, on a per dollar basis, is
Vt(T) = PV¥,t,T[F0(¥/$,T) - Ft(¥/$,T)]=(112.10- 111.8602)/(1 - 0.002)025 = ¥0.239963 per $1
Troubadour’s position is a short position of$1,000,000, so the short position has a positive value of (¥0.239963/$) x$1,000,000 = ¥239,963 because the forward rate has fallen since the contract initiation.
解题思路
这道题第一个计算方法是先计算出t时刻当前市场上no arbitrage的FP,即Ft(T),这个计算方法就是给汇率的远期合约定价的方法(这个计算方法在基础班视频Currency Forward andFutures 这节课有介绍),再与0时刻签订合约的时刻的FP ,即Ft(T)轧差,再往前折现计算出value。也就是答案中的做法。
对这道题来说,因为没有告诉Ft(T),用第二种方法计算更简单易懂。

易错点分析
这道题同学们一个疑惑的点就是不清楚向上箭头和向下箭头怎么画,这里教大家一个方法就是第一步先看汇率报价形式,因为汇率报价形式¥/$,那就是说是买卖美元,第二步是看头寸,short positon,那就是卖美元,卖美元就是支出美元,那么向下箭头表支出就是支出1美元,向上箭头表收入那就是收到112.1日元;
第二个疑惑点就是折现利率选择,因为t时刻距离到期日是3个月,那么向上箭头日元就按3个月的日元利率折现,向下箭头美元就按照3个月的美元利率折现。
第三个疑惑点就是向下箭头折现后为什么要乘以112,因为向下箭头折现后是美元,再乘以t时刻的汇率就转换成了日元,这样向上箭头和向下箭头就可以做差了。
这道题大家还有一个误区就是容易把compounded risk-free rate 当成连续复利,compounded risk-free rate 是复利,continious compounded risk-free rate 才是连续复利。

精选问答7
题干
One month ago, Troubadour purchased euro/yen forward contracts with three months to expiration at a quoted price of 100.20 (quoted as a percentage of par).
The contract notional amount is ¥100,000,000. The current forward price is 100.05. The current annual compounded risk-free rate is0.30%.
The value of Position 2 is closest to:
A. -¥149,925.
B. -¥150,000.
C. -¥150,075.
答案解析
A is correct.
The value of Troubadour’s euro/JGB forward position is calculated as
Vt(T) = PVt,T[Ft(T)– F0(T)]
Vt(T) = (100.05 -100.20)/(1 + 0.0030)2/12= -0.149925 (per ¥100 par value)
Therefore, the value of the Troubadour’s forward position is
Vt (T)= -0.149925/100(¥100,000,000) = -¥149,925
解题思路
这道题是currency forward 合约求value。因为这道题目已经给出了Ft(T),所以我们就可以直接用第一种做法做。
这道题是long position,相当于是0时刻我们签订一份foward合约,约定T时刻买日元的汇率是100.20,而t时刻在市场上签订一份相同到期时间的合约,约定T时刻买日元的汇率是100.05.明显就可以看到我们亏损了,亏损的金额就是100.05 - 100.20再折现到现在。
另外一个理解思路就是此时我们签订一份T时刻卖日元的forward将原来合约平仓平掉,这样T时刻我们卖日元收到100.05,买日元花出去100.20,现在的value就是100.05 - 100.20再折现到现在。
对于这道题而言,由于没有给出当前市场汇率的spot rate,所以我们无法用第二种做法做。
易错点分析
这道题目大家的疑惑点一个是不熟悉汇率的表达形式。汇率的表达形式是A/B,相当于一个B价值多少钱的A,所以我们买卖的对象就是B。对于这道题,报价形式是euro/yen,那么我们买卖(报价)的对象就是日元;
第二个疑惑点是不理解第一种计算方法,也不知道公式里面的字母代表什么意思;
第三个疑惑点就是不知道为什么最后Vt (T)=-0.149925/100(¥100,000,000) = -¥149,925这一步为什么要除以100,除以100主要是因为题目给出的报价是quoted as a percentage ofpar是以面值的百分比报价,相当于是面值为100日元的价格是100.2欧元。

精选问答8
题干
Rocha asks Sousa why the value of a similar in-the-money interest rate call option decreases if the exercise price is higher. Sousa provides two reasons.
![]() Reason 1 The exercise value of the calloption is lower.
Reason 1 The exercise value of the calloption is lower.
![]() Reason 2 The risk-neutral probabilitiesare changed.
Reason 2 The risk-neutral probabilitiesare changed.
Which of Sousa’s reasons for the decrease in the value of the interest rate option is correct?
Reason 1 only
Reason 2 only
Both Reason 1 and Reason 2
答案解析
A is correct.
![]() Reason 1 is correct: A higher exercise price does lower the exercise value (payoff) at Time 2.
Reason 1 is correct: A higher exercise price does lower the exercise value (payoff) at Time 2.
![]() Reason 2 is not correct because the risk-neutral probabilities are based on the paths that interest rates take, which are determined by the market and not the details of a particular option contract.
Reason 2 is not correct because the risk-neutral probabilities are based on the paths that interest rates take, which are determined by the market and not the details of a particular option contract.
解题思路
题目是问为什么利率看涨期权的执行价格升高,看涨期权的价值会降低。因为执行价格升高,exercise value=市场价格-执行价格,所以exercise value 降低,期权的价值降低。
再来看reason 2,reason 2说执行价格升高,看涨期权价值降低的原因是因为风险中性概率的改变。风险概率的大小与执行价格是无关的,风险中性概率是与无风险利率以及u、d有关,
它是由市场决定的,合约中约定的执行价增加并不会引起风险中性概率的变化。所以reason 2不对。
易错点分析
这道题目同学们第一个疑惑点是不知道答案中的exercise value是什么,exercise value是指一个in the money的option在当前时刻行权的价值,比如说我们买入了一个看涨期权,约定以50块钱在T时刻买入中石油股票,如果当前时刻的股价是60的话,那么exercise value=60-50=10块钱。
执行价格升高,执行价值会降低,看涨期权的价值就降低了。第二个疑惑点是大家觉得风险中性的概率变化,call option的价值就会变化,但是对于这道题他问的是为什么执行价格升高,call option的价值降低,而执行价格变化并不能改变风险中性的概率。所以不能从执行价格升高推出来风险中性的概率改变。

精选问答9
题干
Which of the following trades is most likely to accomplish Tzu’s duration objective?
A.Sell interest rate futures.
B:Enter into a pay-fixed interest rate swap.
C:Enter into a pay-floating interest rate swap.
答案解析
C is correct. Tzu’sobjective is to increase the average duration of his bond portfolio from two years to five years. This objective can be accomplished by entering into apay-floating-rate (lower-duration) and receive-fixed-rate (higher-duration)interest rate swap.
A floating-rate bond has a much lower duration than a fixed-rate bond because the floating-rate bond resets periodically as market interest rates change, bringing its market value back to par value。
解题思路
题目是问为如何增加portfolio的duration。那我们就看看哪个头寸能增duration。
![]() A选项,interest rate futures 的标的物是bond,那么sell interest rate futures的duration就等于sell bond 的duration,sell bond,duration减少。不选A。
A选项,interest rate futures 的标的物是bond,那么sell interest rate futures的duration就等于sell bond 的duration,sell bond,duration减少。不选A。
![]() B选项,pay fixed interest rateswap就相当于是short fix rate bond,long floating rate bond,由于fix rate bond 的duration 大于 floating rate bond 的duration ,所以该头寸也会降低duration。
B选项,pay fixed interest rateswap就相当于是short fix rate bond,long floating rate bond,由于fix rate bond 的duration 大于 floating rate bond 的duration ,所以该头寸也会降低duration。
![]() C选项正好和B选项头寸相反,所以会增加duration,所以选C。
C选项正好和B选项头寸相反,所以会增加duration,所以选C。
易错点分析
这道题目第一个疑惑点是不知道interest rate futures 的标的物是bond,以为标的物是interest rate,这样就很容易想反。interest rate futures 的标的物是bond这个我们原版书中也有描述:
Because most interest rate futures contracts are futures contracts in which the underlying is a bond, this type of contract would have a duration that is consistent with the forwardbehavior of the underlying deliverable bond.
第二个疑惑点就是为什么那么sell interest rate futures的duration是负的,duration是衡量利率变化对资产价格影响,如果利率下降,债券价格上升,那么我们就说有一个正的duration,也可以从duration的公式来看,duration=-Δp/p/Δy,当利率与资产价格变化方向相反的时候,有一个正的duration。
接下来我们来看sell interest rate futures,就是sell bond futures。利率上升,bond 价格下降,sell bond futures赚钱。那就是说利率变化与futures value变化方向相同,所以有一个负的duration。所以这里要降低duration的话,就要sell interest rate futures。或者也可以直接把sell interest rate futures理解为拥有一个short bond 的头寸,那就是降低duration。
第三个疑惑点就是为什么pay fixed interest rateswap就相当于是short fix rate bond,long floating rate bond。假设swap期末有一笔本金交换的话,pay fixed interest rate 就是支付固定利率,相当于卖了一个固定利率债券,那收浮动就相当于买了一个浮动利率债券。
第四个疑惑点就是为什么fixed rate bond 的duration 大于 floating rate bond 的duration ,这是因为对于浮动利率债券来说,因为它的coupon是浮动的,所以在每一个reset day也就是coupon day,债券的价值会回归面值。
所以市场利率只会影响两个reset day 期间那段时间的债券价值,而对固定利率债券来说,市场利率对债券发行期间的整个期限的价值都有影响,所以固定利率债券的duration大于浮动利率债券的duration。


