

做过的题你都能拿分吗?

临近考试,小编相信大家都开始启用“题海”战术,疯狂刷题,可是你现在做过的题,你考场碰到都能做对吗?
同为备考党的我,小编只想说,如果只做过一遍,那怕是有点难。

我相信大家都是从题海战术里走出来的朋友们,其实刷题就是一个熟能生巧的事情,即使可能你对某个知识点不理解,但是同一个题型你做完3次后,就有一种闭着眼睛我都能认出你的熟悉感,剥掉题干的外壳,其实都是同一个套路。
那么到底哪些题目是有典型考法,哪些知识点是易错的点,哪些是协会的惯用套路,这就是大家考前需要拿个小本本记下来的事情。
看到这里,是不是大家都有一种蠢蠢欲动,要赶紧去做笔记的想法?

知道目前大家都在争分多秒学习,贴心的品职教研组的小哥哥、小姐姐们也是熬夜赶工(心疼一下),帮大家整理了CFA三个级别学科的错题本,希望在最后的时候能给大家起到助力的作用。
在接下来的几周里,我们会陆续发放三个级别的高频问答,希望对大家的备考有所帮助。今天三级放上固定收益的错题本,大家一起来看看这些题都会做吗?

精选问答1
题干
Easton and Avelyn next discuss credit strategyapproaches. Dynamo uses a bottom-up approach that selects bonds with the best relative value from the universe of bonds with similar characteristics. Avelyn comments on the following considerations in a bottom-up approach.
![]() Comment 1: Callable debt has a smaller option-adjustedspread than comparable non-callable debt.
Comment 1: Callable debt has a smaller option-adjustedspread than comparable non-callable debt.
![]() Comment 2: Benchmark corporate bond issues normally have wider spreads than older bonds of the same issuer.
Comment 2: Benchmark corporate bond issues normally have wider spreads than older bonds of the same issuer.
![]() Comment 3: The announcement of a new corporate bond issue often leads to an increase in the credit spread on the existing bonds.
Comment 3: The announcement of a new corporate bond issue often leads to an increase in the credit spread on the existing bonds.
Which of Avelyn’scomments regarding considerations in the bottom-up approach is most accurate?
A. Comment 1
B. Comment 2
C. Comment 3
答案解析
C is correct. When an issuer announces a new corporatebond issue, the issuer’s existing bonds often decline in value and their spreads widen. This dynamic is often explained by market participants as aneffect of increased supply.
A related reason is that because demand is notperfectly elastic, new issues are often given a price concession to enticeborrowers to buy the new bonds.
This price concession may result in all of an issuer’sexisting bonds repricing based on the new issue’s relatively wider spread. A third reason is that more debt issuance may signal an increase in an issuer’scredit risk.
解题思路
如果能熟知Bottom-up relative-value analysis里的几点考虑因素,本题做起来非常简单,直接套用我们学到的结论即可。
其中A选项错误,原版书上的结论是Callable debt has a larger option-adjusted spread thancomparable non-callable debt.(注:该结论在协会最新发布的勘误里已经勘误了,具体情况看下面的易错点分析)。
B选项也是错误的,正确的结论应该是:Benchmark corporate bond应该比Older bonds有更小的Spread。
C选项正确。同一个发行人新发行债券,会使得已发行债券的Credit spread变大、价格降低。这个结论可以从以下角度理解:
新发行债券,增加了市场的供给,而债券的需求相对稳定,为了使得新发行的债券顺利卖出,往往会“打折”出售,反应出来就是发行人更大的Credit spread,这样,已发行的债券也就需要按照这个更大的Credit spread重新定价,于是导致Existing bond价格下跌、Credit spread上升。
同时,发行人发行更多的债券,也意味着财务质量变差,这样投资者会要求一个更高的Credit spread。
易错点分析
有同学问到为什么原版书上的结论:Callable debt has a largeroption-adjusted spread than comparable non-callable debt是正确的?
按照我们学到的理论,既然是可比债券,那么反映出来的Credit spread应该相等,所以Callable bond的OAS与comparable non-callable bond的OAS应该相等才是,为什么这里说更大也是对的?
理论上说:Callable bond OAS和可比、不含权债券的OAS应该相等,因为OAS反应的是除权利以外债券的其他所有风险。
既然是Otherwise comparable,就说明除了一个含权一个不含权外,两个债券没有其他区别,即其他的所有风险大小一致。这样的话两个的OAS应该相等才是。这是两支债券定价合理情况下的OAS大小。
但是在这个Bottom-up相对分析法下,原版书有这个:“Callable bond OAS比可比的、不含权债券的OAS要更大”这个结论。
原因是虽然理论上两者的OAS应该相等,但是对于Callable bond,因为交易量较小、市场参与度较小,流动性较差,所以往往价格是被低估的,折算出来的OAS要大于其合理值。于是有:Callable bond OAS比可比的、不含权债券的OAS要更大这个结论。
注意这个结论只有在:Bottom-up relative-valueanalysis里成立。没有说在Bottom-up relative-value analysis分析的框架下,我们认为Callable bond OAS等于Comparable non-callablebond OAS。
但是,协会最新一期的勘误把这句结论改了,改成了:callable debtoften has a larger z-spread than otherwise comparable non-callabledebt.
即:Callable bond Z-spread >Comparable non-callable Z-spread.那现在只比Z-spread的话,就更加好比较了,这个就是从二级到现在三级的结论:
因为Z-spread是All-inspread,反应所有风险,对于Callable bond有含权风险以及信用风险(Credit-related risk);对于可比、不含权债券只有信用风险(Credit-related),因为可比,所以两者的信用风险又相等,所以有:
Callable Z-spread > Comparablenon-callable Z-spread
既然协会这么改的话,就忽略原先的结论,估计题目现在也不会提到Callablebond OAS比Comparable non-callable bond更大这条结论了。
现在改动后的这个结论是比较普通的结论,应该是完全没有什么歧义了。
精选问答2
题干
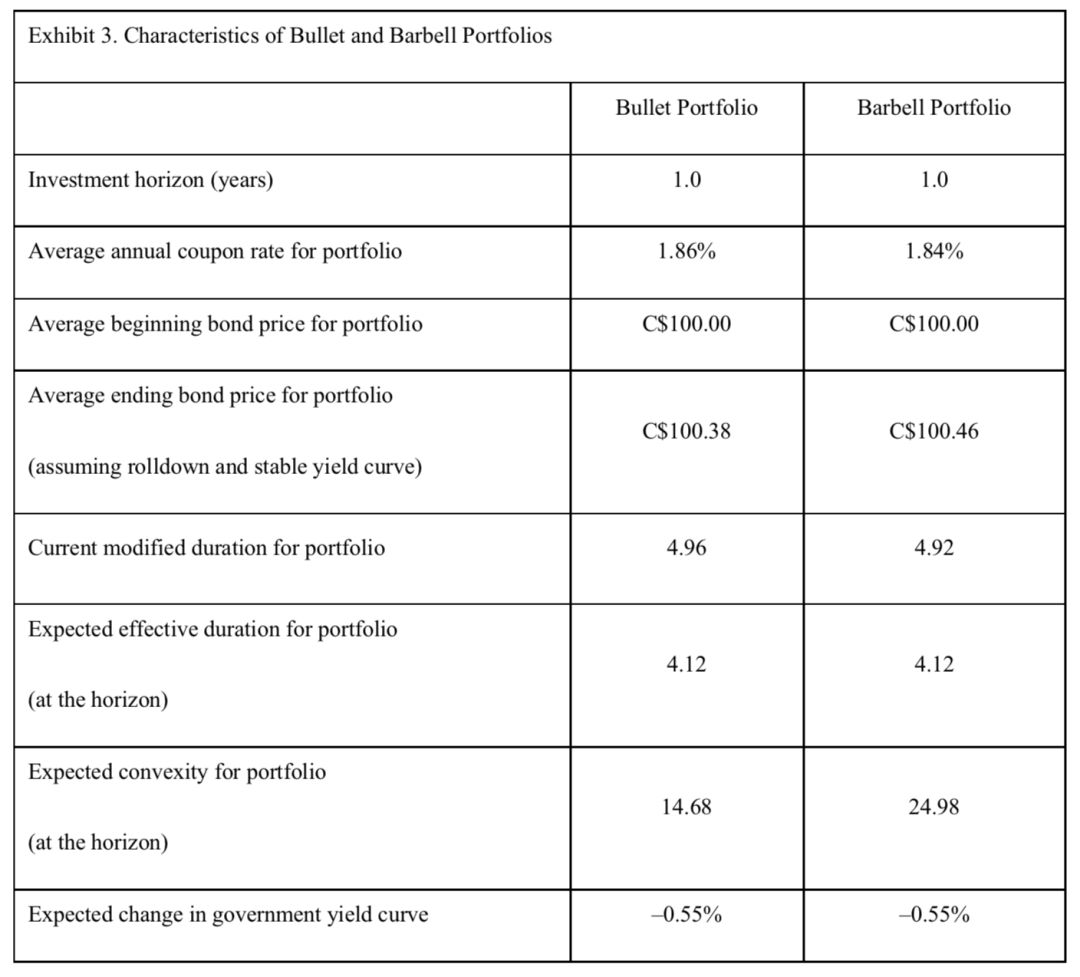
Based on Exhibit 3, the total expected return of Hirji’s barbell portfolio is closest to:
A. –2.30%
B. 0.07%
C. 4.60%
答案解析
C is correct. The total expected return is calculated as follows:
Yield income = Annual coupon payment/Current bond price = 1.84/100.00 = 1.84%
Rolldown return = (Bond priceeh – Bond pricebh)/Bondpricebh = (100.46 – 100.00)/100.00 = 0.46%
E(change in pricebased on yield view) = (–MDeh × Δyield) + [1/2 × Convexity × (Δyield)2] = [–4.12 × (–0.55%)] +[1/2× 24.98 ×(–0.55%)2]= 2.30%
解题思路
本题按照收益率分解公式进行计算即可。但是需要注意的是,由于本题表格里给了2个Duration数据(Modified duration与Effective duration),所以在计算时,需要筛选一下。
易错点分析
有同学问到:本题为什么要使用Effective duration而不是使用Modified duration。关于Effective duration和Modified duration,两个其实表达的意思一样,都可以衡量利率变动的敏感度,但是使用的范围有一些不同。一般情况,题目给哪个就用哪个。
但有一些情况,只能用Effective duration,例如,当组合里面有含权债券或者浮动利率债券(Floater)时,只能用Effective duration,因为这两类债券没有一个有效的Modified duration数据,只能求一个Effective duration。
第二点就是,求E(changes in price base oninvestor's view of yields and yield spread)时,用到的Duration数据应该是利率变动时的Duration数据,即一个未来的Duration数据。
因为是预期利率在未来变动,所以应该使用未来预期的Duration数据,注意本题Modified duration是Current modified duration是当前的Duration数据,所以不可用。而Effective duration时期末的Duration数据是一个未来值可以用。
其实,更精确的是使用利率变动时的Duration,但其实是站在当前算未来收益,将来什么时候变也不知道。所以有些题目就直接给了Average modified duration。
总结下就是:两个Duration都可以用,给哪个用哪个。两个都给的话,看组合有没有含权债券和Floater,有的话只能用Effective duration。因为是预测利率变动,所以只能用未来时间的Duration数据。
精选问答3
题干
Inter-market trade strategies和carry trade之间是什么关系?
解题思路
Inter-market trade strategies是大范畴的概念。最简单的,投资于Homecountry之外的市场,就算Inter-market trade strategies,比如中国基金投资在美国市场。
所以,我们在三级固定收益学过的所有策略:
![]() Stable yield curve下的策略:Buy-and-hold、Riding the yield curve、Sell convexity,Carry trade
Stable yield curve下的策略:Buy-and-hold、Riding the yield curve、Sell convexity,Carry trade
![]() 以及Unstable yield curve下的策略:Buy Convexity、duration management,Barbell/Bullet/Condor/Butterfly、Buy convexity
以及Unstable yield curve下的策略:Buy Convexity、duration management,Barbell/Bullet/Condor/Butterfly、Buy convexity
这些策略如果使用在国外市场,都可以称为是Inter-market tradestrategies。
而如果在两国间做Carry trade,则该Carry trade属于Inter-market carry trade,属于Inter-market strategies。
易错点分析
在做题目时,注意看题干是Inter-market trades,还是Inter-market carry trades,两者差一个字,但是意思不同。如果将题干看错,可能会得到错误的结论。
精选问答4
题干
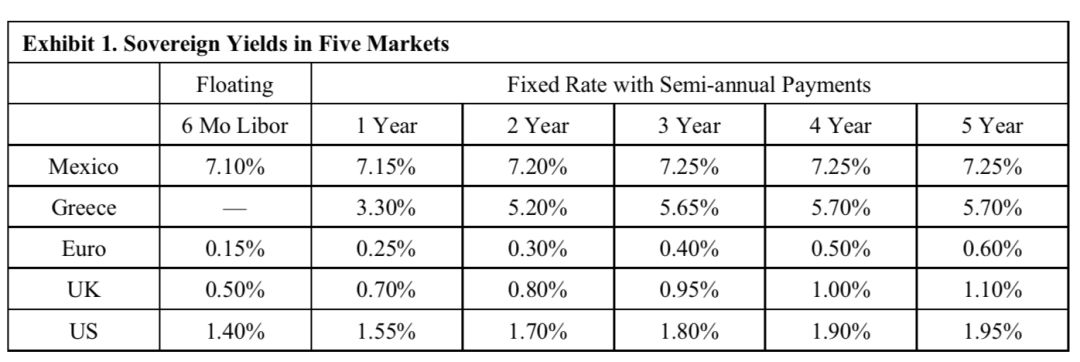
Winslow thinks the Mexican and Greek markets may offer attractive opportunities to enhance returns. Yields in these markets are given in Exhibit 1, along with those for the base currencies of her portfolios.
The Greek rates are for euro-denominated government bonds priced at par. In the other markets, the yields apply to par sovereign bonds as well as to the fixed side of swaps versus six-month Libor (i.e., swap spreads are zero in each market). The six-month Libor rates also represent the rates at which investors can borrow or lend in each currency.
Winslow observes that the five-year Treasury-note and the five-year German government note are the cheapest to deliver against their respective futures contracts expiring in six months.
Winslow expects yields in the US, Euro,UK, and Greek markets to remain stable over the next six months. She expectsMexican yields to decline to 7.0% at all maturities.
Meanwhile, she projects that the Mexican Peso will depreciate by 2% against the Euro, the US Dollar will depreciate by 1% against the Euro, and the British Pound will remainstable versus the Euro. Winslow believes bonds of the same maturity may beviewed as having the same duration for purposes of identifying the mostattractive positions.
Based on these views, Winslow is considering three types of trades.
![]() First, she is looking at carry trades, with or without taking currency exposure, among her three base currency markets. Each such trade will involve extending duration (e.g., lend long/borrow short)in no more than one market.
First, she is looking at carry trades, with or without taking currency exposure, among her three base currency markets. Each such trade will involve extending duration (e.g., lend long/borrow short)in no more than one market.
![]() Second, assuming the legal department confirms her interpretation of permissible currency hedging, she wants to identify the most attractive five-year bond and currency exposure for each of her threeportfolios from among the five markets shown in Exhibit 1.
Second, assuming the legal department confirms her interpretation of permissible currency hedging, she wants to identify the most attractive five-year bond and currency exposure for each of her threeportfolios from among the five markets shown in Exhibit 1.
![]() Third, she wants to identify the most attractive five-year bond and hedging decision for each portfolio if she is only allowed to hedge into the portfolio’s base currency.
Third, she wants to identify the most attractive five-year bond and hedging decision for each portfolio if she is only allowed to hedge into the portfolio’s base currency.
Considering only the US, UK, and Euro markets, the most attractive duration-neutral, currency-neutral carry trade could be implemented as:
A. Buy 3-year UK Gilts, Sell 3-year German notes, and enter a 6-month FX forward contract to pay EUR/receive GBP.
B. Receive fixed/pay floating on a 3-year GBP interest rate swap and receive floating/pay fixed on a 3-year EUR interest rate swap.
C. Buy the T-note futures contract and sell the German note futures contract for delivery in six months.
解题思路
按照我们三级这种题型的解题思路:看到题干是Currency neutral,Duration neutral,most attractive carry trade,这里有三个要求:
要求1. Currency neutral,要达到Currencyneutral,就要保证Carry trade是在一个市场上做的。即借低利率投高利率再一个市场上完成,这样就不涉及货币问题。但是,这里会获得一个净的正Duration头寸。
要求2. Duration neutral,因为上面要求1获得了净的正Duration头寸,要保证Duration neutral,就需要在另外一个市场上,做一个反向负的Duration的策略,这样两个市场合起来就能满足Duration-neutral。
要求3. 第三个要做到Most attractive,即收益最大,这样就要在要求1里面的Carry trade收益要最大,同时2里面用来对冲Duration策略的损失最小,这样两个市场上合起来的净收益最大。这是这类道题的题干要求,也是解题思路。
![]() 满足第一个要求,同时获得最大收益的Carry trade,就是找哪个国家的收益率曲线最陡峭,本题就是UK市场上的最陡峭,所以做Carry trade选UK市场;
满足第一个要求,同时获得最大收益的Carry trade,就是找哪个国家的收益率曲线最陡峭,本题就是UK市场上的最陡峭,所以做Carry trade选UK市场;
![]() 第二个要求,做Duration neutral策略,这个要求就是为了对冲Duration,所以损失越小越好,就是找哪个收益率曲线最平缓,最Flattest的收益率曲线,这样构建出负的Duration,同时收益率损失比较小,本题就是EUR。
第二个要求,做Duration neutral策略,这个要求就是为了对冲Duration,所以损失越小越好,就是找哪个收益率曲线最平缓,最Flattest的收益率曲线,这样构建出负的Duration,同时收益率损失比较小,本题就是EUR。
找到了两个市场,就要选期限了。找两个市场上哪个期限上的收益率差最大,发现是3年期UK和3年期EUR的差最大,是0.55%。
所以最终的策略是:
![]() 第一组:invest 3-year UK,borrow 6-monthUK;
第一组:invest 3-year UK,borrow 6-monthUK;
![]() 第二组:borrow3-year EUR,invest 6-monthEUR;
第二组:borrow3-year EUR,invest 6-monthEUR;
第一组UK市场实现Carry trade;第二组EUR市场实现Duration neutral。因为又是在同一个市场上借贷,所以又是Currency-neutral,这样实现了题干的3个要求。
这种策略之所以可以看成是Inter-market carry trade,是因为换个角度看,这种策略等同于:
Invest 3-year UK, borrow3-year EUR;同时borrow 6-month UK, invest6-month EUR。
根据A/B/C三个选项,B选项可以获得以上利率的头寸。
易错点分析
A选项错误的原因是Forward合约的方向反了,应该是进入:Pay GBP / Receive EUR这个合约。
A选项中已经买入了三年期UK债券:Buy 3-year UK Gilts, 卖出了3年期德国债券: Sell 3-year German notes;所以剩下一个借UK 6 month,投资EUR 6-month。可以利用6-month Currency forward构建出这个利率头寸,如果要构建一个借UK6 month,投资EUR 6-month,就需要进入PayGBP / Receive EUR的合约。
A选项的Forward刚好相反。C选项错误的原因是Buy the T-note futures contract,选择了US市场做Carry trade,根据表格UK市场收益率曲线最陡峭,所以应该选择UK市场做Carry trade。
精选问答5
题干
The second project for Soto is to help Hudgens immunize a $20 million portfolio of liabilities. The liabilities range from 3.00 years to 8.50 years with a Macaulay duration of 5.34 years, cash flow yield of 3.25%, portfolio convexity of 33.05, and basis point value (BPV) of $10,505.
Soto suggested employing a duration-matching strategy using one of the three AAA rated bond portfolios presented in Exhibit 2.
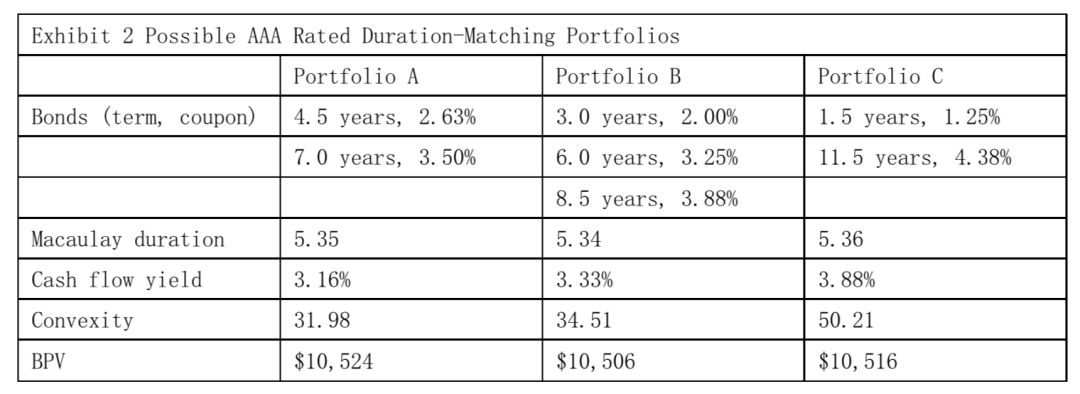
Based on Exhibit 2, the portfolio withthe greatest structural risk is:
A. Portfolio A.
B. Portfolio B.
C. Portfolio C.
解题思路
Structural risk反应收益率曲线非平行移动时,资产组合不能匹配负债的风险。这种风险是由资产组合现金流分布带来的。其中其他条件相等,现金流越分散的资产组合,用其匹配负债时,Structural risk越大。而资产组合的Convexity数据与组合现金流的分散程度成正向关系。
这样的话,判断Structural risk时,就要看资产的Convexity数据。在Macaulay duration数据、Cash flow yield数据相近的情况下,Convexity越大,资产的Structural risk越大。根据表格内的信息,Structural risk最大的债券组合为Portfolio C,所以Portfolio C的Structural risk最大。
易错点分析
有同学问到,Convexity是债券的优质属性,具有涨多跌少的性质,那为什么在Duration-matching策略里面,我们还需要找Convexity最小的资产组合来降低Structural risk呢?
其实,单看债券投资,Convexity是可以提供债券涨多跌少的好处。也就是说,一般在做主动管理时,如果预测收益率曲线波动加大,那么相同条件下,Convexity更大的债券,其表现会更好。
但是在做Matching liability时,我们追求的目标不是享受Convexity带来的涨多跌少的好处,而是尽可能地使得资产的变动和负债的变动相Match,使得资产能够匹配负债。
而在做Duration-matching时,资产的Convexity越大,匹配时Structural risk越大,即在收益率曲线非平行移动时,资产不能匹配负债的风险越大。
为了降低Duration-matching时不匹配的情况,就需要尽可能的降低资产的Convexity数据。
也就是说,Convexity虽然有涨多跌少的好处,但是在Duration matching时,不需要这个好处,Convexity过大反而会带来风险(Structural risk)。
这样的话,在做单期负债匹配时,我们就要求了资产的Convexity尽可能的小。
而在做多期负债匹配时,我们要求资产的Convexity值在大于Liability convexity值的基础上,又尽可能的降低资产的Convexity,实际上也就是在要求资产的Convexity数据足够地贴近负债的Convexity数据,降低资产负债不匹配的风险。
精选问答6
题干
Based on Exhibit 2, relative to Portfolio C, Portfolio B:
A. has higher cash flow reinvestmentrisk.
B. is a more desirable portfolio forliquidity management
C. provides less protection from yieldcurve shifts and twists.
解题思路
本题和上一题的题干信息相同。从表格中发现,由于Portfolio B与Portfolio C的Macaulay duration相近,而Portfolio C投资于1.5 years和11.5 years债券,而Portfolio B投资于3.0 years、6.0 years、8.5 years债券。
两个组合的现金流分布不同,这样相比,Portfolio B为一个Laddered portfolio,而Portfolio C为一个Barbell portfolio。所以根据Portfolio structure类型,很容易判断出B选项是正确的。
易错点分析
有很多同学错选C选项。C选项刚好说反了。
应该是Portfolio B能够提供更多的保护,因为Portfolio B的Convexity比Portfolio C的Convexity更小。
在其他条件一定的情况下,Convexity越小的债券,在收益率曲线Twists和Shifts时,提供的保护越多。
注意C选项是Protection from yield curve shifts and twists,这里是包括收益率曲线的非平行移动。
精选问答7
题干
Edgarton expects a steepening yield curve, with short-term yields rising by 1.00% and long-term yields rising by more than 1.00%. He evaluates the Fund’s positions from Exhibit 1 along with two of his pro forma portfolios, which are summarized in Exhibit 2:
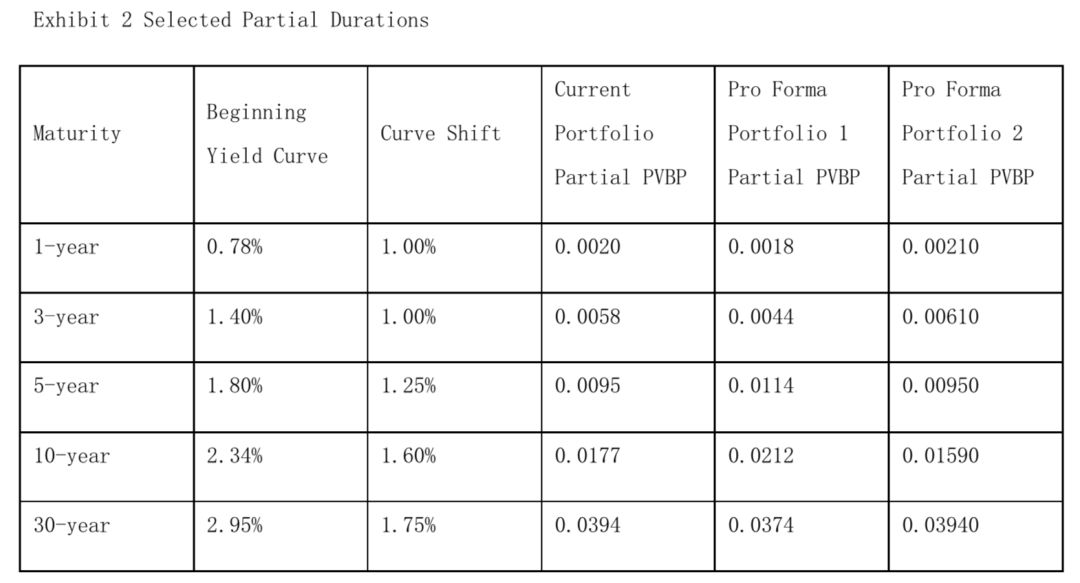
Based on Exhibits 2, which of thefollowing portfolios is most likely to have the best performance givenEdgarton’s yield curve expectations?
A. Current Portfolio
B. Pro Forma Portfolio 1
C. Pro Forma Portfolio 2
解题思路
虽然在我们可以通过债券组合Partial PVBP的分布,来判断债券组合的类型是Barbell/Bullet,还是Laddered,进而判断在收益率曲线Steepening/Flattening时,表现的好坏。
但注意,如果要套用结论,需要保证收益率曲线只有单纯的Steepening/Flattening变动、或者三个组合的整体Duration数据一样。
注意看Exhibit2里面的数据,Curve shift的数据如下:
1-year:1.00%
3-year:1.00%
5-year:1.25%
10-year:1.60%
30-year:1.75%
从上面数据看出,这不仅仅是Yield curve steepening,其实可以进一步拆解成收益率曲线整体向上平移1%,然后5-year再额外上升0.25%,10-year再额外上升0.60%,30-year再额外上升0.75%。
所以这个收益率曲线的变动实际上是:Yield curve upward shift + Yield curve steepening;
如果要利用收益率曲线Steepening/Flattening/Curvature变动,Bullet和Barbell哪个表现更好的结论,要么需要保证收益率曲线的变动只有Steepening,而没有平行移动;要么一定要保证这两个Portfolio整体的Duration是一样的。
因为涉及到平行移动以及Steepening变动,所以如果两个Portfolio的整体Duration不同的话,并不能简单的说Steepening就是Bullet最好。因为Duration会影响组合的表现、现金流分布(Bullet/Barbell)也会影响组合的表现,且两者的影响方向不一定相同。
比如说,Steepening的确是Bullet表现更好,但是本题Bullet型Portfolio的总Duration又最大,平行上移时,该Portfolio表现又最差。所以在平行移动+Steepening的变动下,很难说这个Bullet是否表现最好。
这道题的解法,是以Current portfolio为Benchmark,因为Portfolio 2表现比Current更好,Portfolio 1比Current表现更差,所以整体而言是Portfolio 2更好。
因为Portfolio2的长端Partial PVBP比Current小,短端比Current更大,所以在这种收益率曲线的变动下,Portfolio 2表现更好;
因为Portfolio1的短端Partial PVBP比Current小,长端比Current更大,所以这种收益率曲线的变动下,Current又更好;综合一下是Portfolio 2更好。
当然,本题也可以用简单粗暴的方法:直接计算,看看哪个Portfolio的表现最好。
易错点分析
在套用Steepening/Flattening/Curvature改变,Barbell/bullet/laddered型组合哪个表现更好的结论时,一定要保证三个组合的整体Duration相等,这样表现好坏的差异只来自现金流分布的不同,而不是其他原因。或者要保证Steepening/Flattening一定是拆分到最小单位的变动,不包括平行移动。


