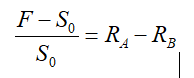问题如下:
Considering only the US, UK, and Euro markets, the most attractive duration-neutral, currency-neutral carry trade could be implemented as:
选项:
A.Buy 3-year UK Gilts, Sell 3-year German notes, and enter a 6-month FX forward contract to pay EUR/receive GBP.
B.Receive fixed/pay floating on a 3-year GBP interest rate swap and receive floating/pay fixed on a 3-year EUR interest rate swap.
C.Buy the T-note futures contract and sell the German note futures contract for delivery in six months.
解释:
B is correct.
In order to be duration-neutral and currency-neutral, the trade must lend long/borrow short in one market and do the opposite (lend short/borrow long), with the same maturities, in another market. The best carry is obtained by lending long/borrowing short on the steepest curve and lending short/borrowing long on the flattest curve. The GBP curve is the steepest and the EUR curve is the flattest. The largest yield spread between these markets is 0.55% at the 3-year maturity, and the narrowest spread is 0.35% at the 6-month maturity. Hence, the best trade is to go long the GBP 3-year/short the EUR 3-year and long the EUR 6-month/short the GBP 6-month. This can be implemented in the swaps market by receiving 3-year fixed/paying 6-month floating in GBP and doing the opposite in EUR (receiving 6-month floating/paying 3-year fixed). The net carry is +0.10% = [(0.95% – 0.50%) + (0.15% – 0.40%)]/2 for six months.
A is incorrect. The FX forward position as stated (pay EUR/receive GBP) corresponds to implicitly borrowing EUR for six months and lending GBP for six months. Correct execution of the trade would require the opposite, receiving EUR and delivering GBP 6 months forward.
C is incorrect. This combination of futures positions does create a duration-neutral, currency neutral carry trade, but it is not the highest available carry. Since the T-note futures price reflects the pricing of the 5-year note as cheapest to deliver, the long position in this contract is equivalent to buying the 5-year Treasury and financing it for 6 months. This generates net carry of 0.275% = (1.95% – 1.40%)/2. Similarly, the short position in the German note futures is equivalent to being short the 5-year German note and lending the proceeds for 6 months, generating net carry of –0.225% = (0.15% – 0.60%)/2. The combined carry is 0.05%, half of what is available on the position in B.
请问为什么A选项的forward的方向错了呢?看答案的解释没转过来。。。