NO.PZ2023090401000078
问题如下:
Question A bond fund manager has requested quotes from a bond dealer on two bonds, Bond X and Bond Y, with the same maturity date and coupon rate. The dealer informs the manager that Bond X trades at a spread of 30 bps over the Treasury market, while Bond Y trades at a spread of 70 bps. Which of the following statements is a correct conclusion for the manager to make?
选项:
A.
Bond X earns a lower return than that of the comparable Treasury bond, since its spread serves to increase the discount rate of its cash flows.
B.
The price of Bond X is currently higher than the price of Bond Y.
C.
To equate the present value of Bond Y’s cash flows to its face value, 70 bps would need to be added to the yield to maturity of a Treasury bond with comparable maturity.
D.
The spread differential indicates that there is a 0.4% difference in price between Bond X and Bond Y.
解释:
Explanation:
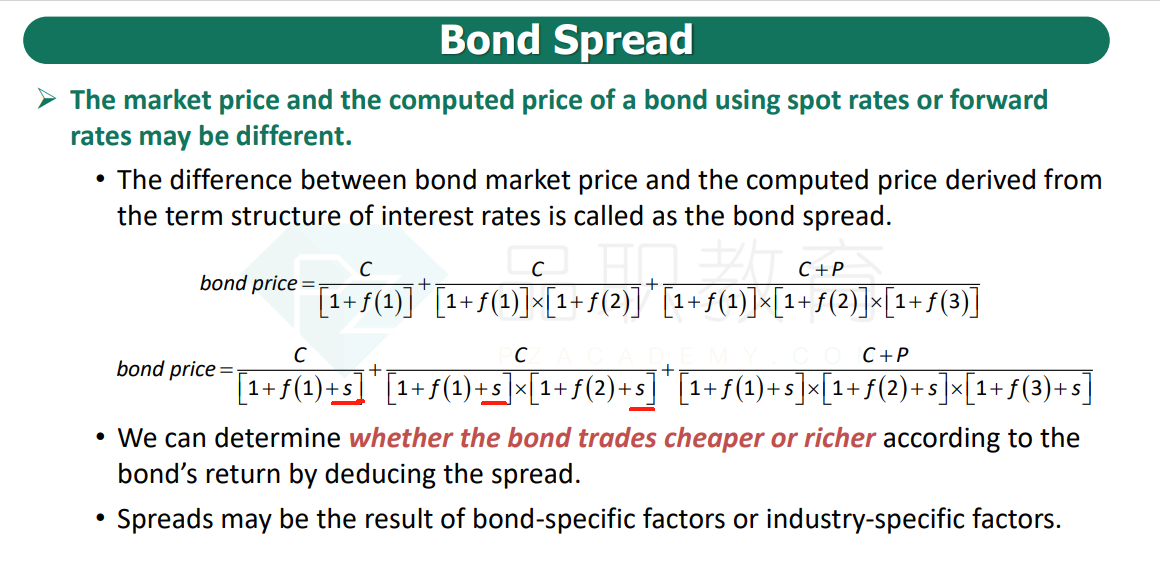
B is correct. Spread is a measure of the excess return earned on a bond over the return provided by a reference security or securities (e.g. Treasury securities). Because the cash flows offered by the reference security are discounted by the appropriate forward rates, adding a spread to these rates serves to decrease the corresponding discount factors. The larger the spread, the greater the decrease in the discount factors, therefore the lower the bond price. Thus, the price of Bond Y (with its 70 bps spread) is lower than the price of Bond X (with its 30 bps spread).
A is incorrect. As mentioned above, spreads can be interpreted as the excess return earned over the return provided by the comparable reference security. Bond X’s positive spread indicates a higher return than the Treasury bond.
C is incorrect. Spreads are applied to the forward rate curve of the reference security, not its yield to maturity.
D is incorrect. This is not a valid application of spreads.
Section: Valuation and Risk Models
Learning Objective: Define and interpret the spread of a bond and explain how a spread is derived from a bond price and a term structure of rates.
Reference: Global Association of Risk Professionals. Valuation and Risk Models. New York, NY: Pearson, 2022. Chapter 11. Bond Yields and Return Calculations
老师好,能否翻译一下C选项的中文和答案对C选项的解释?