NO.PZ2024011002000136
问题如下:
A company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with IFRS incurred and capitalized €2 million of development costs during the year. These costs were fully deductible immediately for tax purposes, but the company is depreciating them over two years for financial reporting purposes. The company has a long history of profitability, which is expected to continue. Which is the most appropriate way for an analyst to incorporate the differential tax treatment in his analysis? He should include it in:选项:
A.liabilities when calculating the company's current ratio. B.equity when calculating the company's return-on-equity ratio. C.liabilities when calculating the company's debt-to-equity ratio.解释:
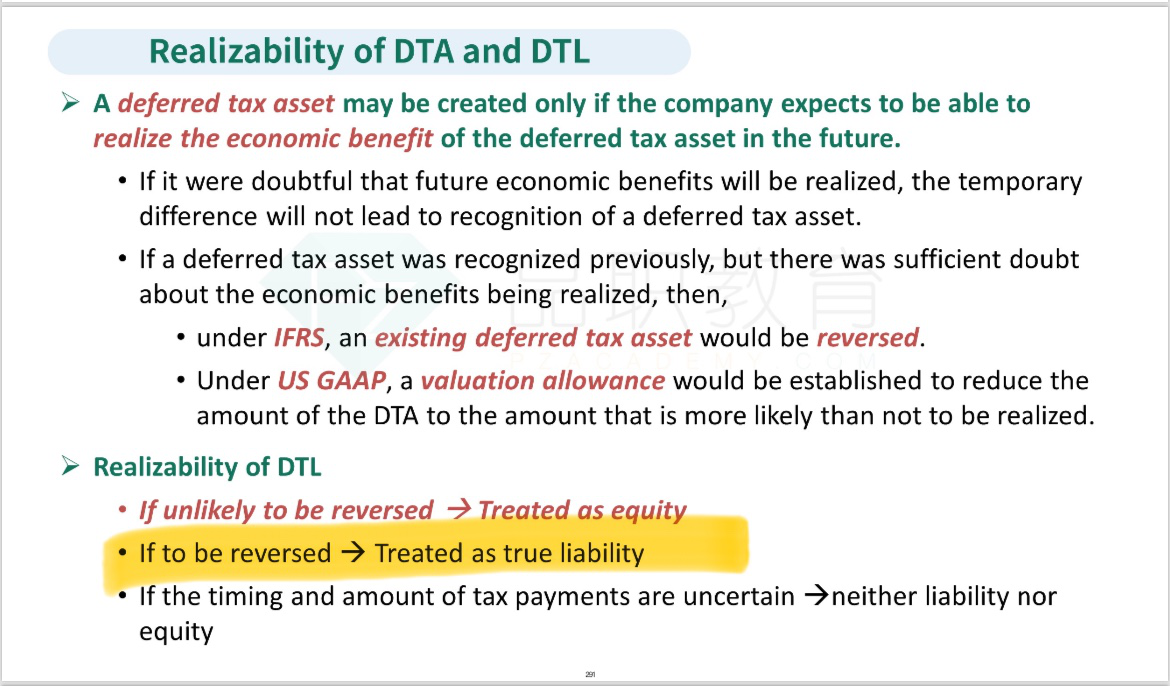
The different treatment for tax purposes and financial reporting purposes is a temporary difference and would create a deferred tax liability. Deferred tax liabilities should be classified as debt if they are expected to reverse with subsequent tax payments. The long history of profitability implies the company will likely be paying taxes in the following years, and hence an analyst could reasonably expect the temporary difference to reverse. Under IFRS, all deferred tax liabilities are non-current.能解释下吗