

做过的题你都能拿分吗?

临近考试,小编相信大家都开始启用“题海”战术,疯狂刷题,可是你现在做过的题,你考场碰到都能做对吗?
同为备考党的我,小编只想说,如果只做过一遍,那怕是有点难。

我相信大家都是从题海战术里走出来的朋友们,这其实就是一个熟能生巧的事情,即时可能你对某个知识点不理解,但是同一个题型你做完3次后,就有一种闭着眼睛我都能认出你的熟悉感,剥掉题干的外壳,其实都是同一个套路。
那么到底哪些题目是有典型考法的,哪些知识点是比较易错的点,这就是大家考前需要拿个小本本记下来的事情。
看到这里,是不是大家都有一种蠢蠢欲动,要赶紧去做笔记的想法?

知道目前大家都在争分多秒学习,贴心的品职教研组的小哥哥、小姐姐们也是熬夜赶工(心疼一下),帮大家整理了CFA三个级别学科的错题本,希望在最后的时候能给大家起到助力的作用。
在接下来的几周里,我们会陆续发放三个级别的高频问答,希望对大家的备考有所帮助。今天二级放上FSA的错题本,大家一起来看看这些题都会做吗?
二级财务的框架非常清晰,一共分为6个reading、5大部分,它们分别为:公司间投资、养老金、外币会计、金融机构分析以及报表分析。其中Reading 17 Analysis of financial institutions是今年新增的一个章节。整章以定性结论为主,并不算是难点。


精选问答1
题干
Fabian, CFA, work on the Equity investment company,Fabian is preparing a research report on PZ Company, listed in HK and complies with IFRS. She collected a part of information from PZ company’s 2018 financial report in the following table (assume cost=par value):
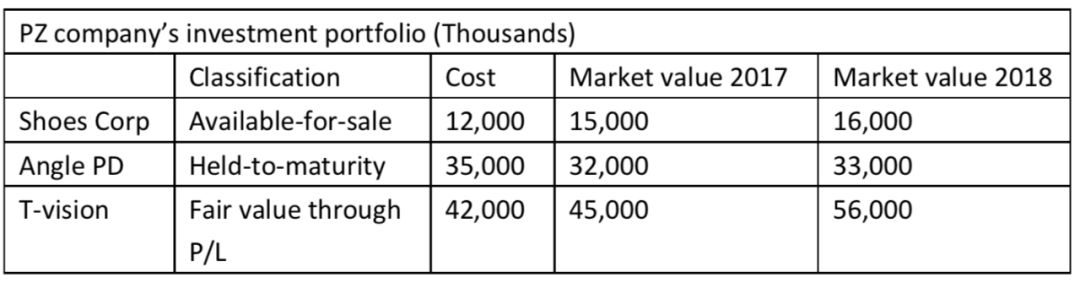
If Angle PD had been reclassified asavailable-for-sale, the interest income would be:
A. higher
B. the same
C. lower
答案解析
B is correct.
解题思路
无论是held-to-maturity还是available-for-sale,期间收益都是计入I/S的。债券的interest income=期初amortized cost*discount rate,amortized cost是债券的摊余成本,通常我们可以通过BASE法则计算出来,discount rate是债券发行时的有效利率,而不是当下的市场利率。
不管债券被划分为哪种金融资产,都不会影响其摊销过程,如果bond划分为HTM,那么其carrying value是amortized cost,如果bond被划分为AFS或者TS,则以fair value入账,账面价值会随着fair value的改变而改变,但是债券折价或溢价的摊销过程仍然是从债券发行时的价格向其面值回归的过程,还是正常按照BASE法则的过程进行逐年摊销。
比如溢价购买的债券,购买价格是1051,那么在债券到期之前,债券的amortized cost就从1051变成1000,这个过程是不受到金融资产分类的影响的。
摊销过程中的B就是期初的1051,A和S就是当年的interest和coupon,interest就是用期初的1051乘以发行时的discount rate算出来的,coupon就是用面值乘以coupon rate算出来的,债券即使被分类为AFS或者TS,这个摊销的计算过程还是这样,计算结果也一样,因为计算过程中使用的要素都没有改变,只不过amortized cost不再体现在carrying value上了。债券不管怎么划分,amortized cost和discount rate都不受到影响,因此interest income也不会改变。
易错点分析
这道题做错的话说明对债券的摊销问题理解不到位,债券之所以有摊销的问题,是因为在发行的时候存在溢价发行和折价发行,发行时市场利率和coupon rate不同导致后续实际收到的现金流和基于权责发生制应该计入I/S的利息不同,这个差异要在债券的存续期间摊销。
由于这个差异的来源是发行时的市场利率,和债券购买之后的市场利率无关,因此摊销也是用的发行时的利率和价格。要明确:
![]() 债券的摊销过程不受到金融资产分类的影响;
债券的摊销过程不受到金融资产分类的影响;
![]() interest income的计算也是债券摊销过程的一部分,也不会受到金融资产分类的影响。
interest income的计算也是债券摊销过程的一部分,也不会受到金融资产分类的影响。

精选问答2
题干
On 1 January 2012, Eagleacquired 20% of the voting shares of Aurora Aerospace Inc. (Aurora). Auroramanufactures the landing gear used in Eagle’s planes. Details about theinvestment and Aurora are in Exhibit 2.
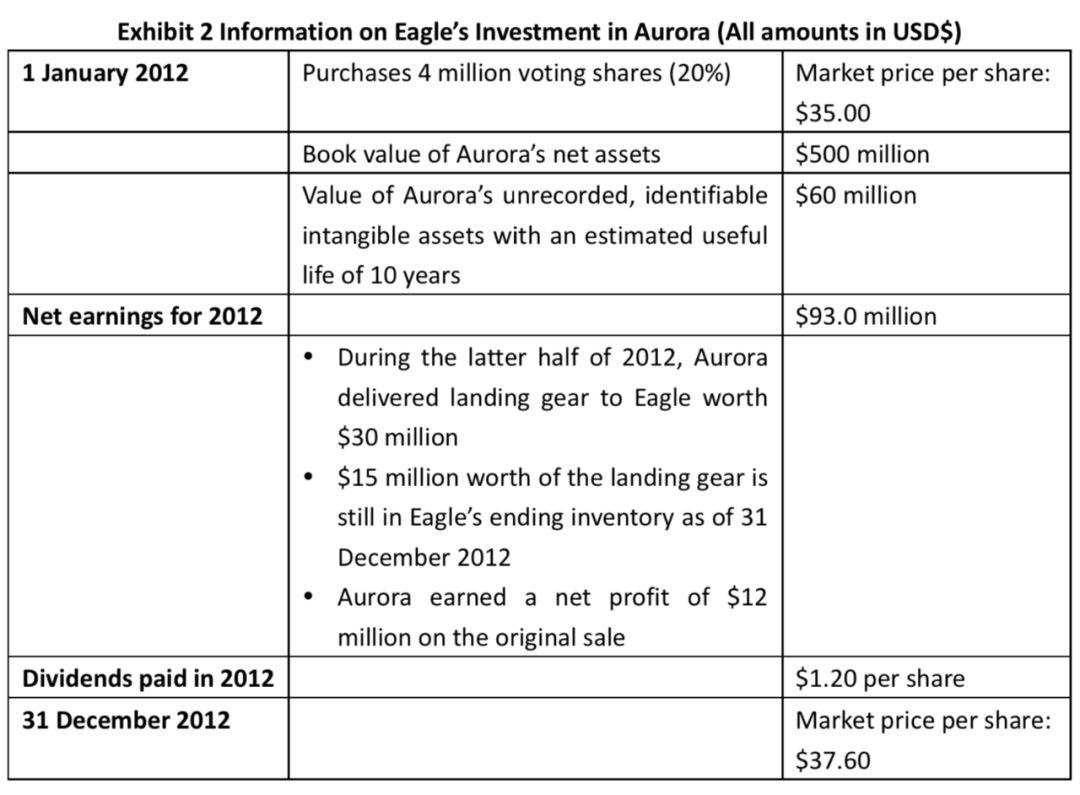
(1)If Eagle uses the equity method, the income ($ millions) from its investment in Aurora for 2012 will be closest to:
A. 16.2.
B. 17.4.
C . 21.0.
(2) If Eagle uses the fair value method, the income ($ millions) from its investment in Aurora for 2012 will be closest to:
A. 4.8.
B. 10.4.
C. 15.2.
答案解析
(1)A is correct.
From the initial acquisition, Eagle’s share of the unrecorded identifiable intangible assets is $60 million × 20% = $12 million. This amount will have to be amortized against investment income over its useful life of 10 years (12/10 = 1.2 per year).

(2)C is correct.
Unrealized gain from the change in fair value:(37.60 – 35.00) × 4 million shares = 10.4
Dividend income: 1.20 × 4 million shares =4.8
Total investment income =$15.2
解题思路
第一问用equity method,要先对A公司的NI进行fair value的调整,然后再乘以持股比例合并到E公司NI中。2012年A公司的NI是93 million,有一个unrecorded identifiable资产需要摊销,因此要从NI中减掉60/10=6的摊销费用,还涉及到关联交易需要调整unrealized profit,先算出profit margin=12/30=40%,当年有15million没有向第三方出售,对应的unrealized profit=15×40%=6million。调整后的NI=93-6-6=81,然后再乘以持股比例20%,E公司应该合并A公司的NI=81×20%=16.2 million。
第二问的fair value method和trading securities的处理方法相同,从年初到年底,A公司股票价格从35涨到37.6,E公司拥有A公司4 million股票,且E公司收到了分红1.2 per share,因此E公司投资A公司所获得的收益=(37.6-35)×4+1.2×4=15.2million。
易错点分析
这两个小问可以结合起来看,第一问是equity method,第二问是fair value option,很多同学对于equity method下dividend处理不理解,问题集中在“为什么dividend不影响合并的NI”。
这是因为分红是在公司获得NI之后进行的,也就是从NI里面出的钱,Equity method下,母公司获得的dividend就是从合并过来的NI里面出的,如果再加一遍dividend,就重复计算了,因此会计准则对dividend的处理,是要求在B/S上的investment in associate中扣减,同时增加cash。
第二问用的是fair value method,有的同学问为什么这道题中就加了dividend,因为这个方法和trading securities的处理方法一样,要考虑fair value的变化以及dividend,fair value method不合并子公司的NI,不会发生重复计算问题。

精选问答3
题干
Inside the offices of Panorama Investment Partners, Aisha Ishmael and Liam Lenihan, principals at thefirm, are meeting to discuss some investment decisions for their flagship equityfund.
The two companies they are discussing are networking equipment makers,Zip Technologies Ltd.(ZipTech) and Euronet GmBH (Euronet), both of which recently reported resultsfor the fiscal year ending 31 December 2017.
Ishmael asks Burgess, “What have you come across withrespect to the companies’ post-retirement benefits?”
Burgess replies, “I noticed that both companies are reporting net pension liabilities. Both companies amended their defined benefit pension plans during the year that just ended, providing enhanced benefits onpast service to retain key technical employees.
But I don’t understand why Euronet’s pension expenses were proportionately much higher year over year thanwere those of ZipTech, because both companies have similar workforces and the pension benefits were on par both before the amendments and after.”
Lenihan responds, “I think it’s because ZipTech reports under US GAAP while Euronet reports under IFRS and because of how those reporting frameworks account for past service costs.”
Lenihan’s response about the difference in ZipTech’sand Euronet’s pension costs is most likely:
A. correct because Euronet would have reported past service costs in net income immediately.
B. incorrect because ZipTech’spast service costs are reported in OCI and are not subsequently amortized tonet income.
C. incorrect because both companies would have accounted for pension costs in the same way.
答案解析
A is correct.
Lenihan is correct. Under IFRS (Euronet), past service costs are reported in net income in the year of the decision. Under US GAAP(ZipTech), they are reported in OCI and amortized to net income over the service life of the employees.
As a result, in the year of the decision towards past service costs, the past service costs reported in net income underUS GAAP are a fraction of those reported under IFRS.
解题思路
两个公司都修改了养老金计划,而且两个公司其他有关养老金的特点也很相似,但是E公司的pension expenses要比Z公司的多。看到修改养老金计划,应该能马上想到past service cost,美国准则和国际准则下的会计处理是不同的,国际准则下的全部psc都确认在I/S中,而美国准则是把psc确认在OCI里,然后在I/S中摊销,因此国际准则的I/S包含的是所有的psc,而美国准则的I/S包含的是摊销的psc,摊销的psc肯定比psc少,所以是国际准则下的expense更大。
易错点分析
这是2019年的一道MOCK题,知识点本身很基础,只是对于这道题的表述在理解上需要花点时间。这道题中主要影响两个公司pension expense的是psc,另外还有一个影响因素是国际准则和美国准则下expected return的区别。
国际准则下pension expense里包含的是“E(R)”,之所以加引号因为它不是真正expected return,而是用计算PBO时所用的discount rate乘以期初plan asset计算出来的,discount rate用的是公司高质量债券的收益率,债券的收益率一般都小于真正的资本市场的expected return,也就是美国准则下的E(R)。
由于国际准则下的E(R)小于美国准则下的E(R),而E(R)的增加会减少net interest expense,所以国际准则下的pension cost更大。综合psc和expected return两项的影响,能判断出Lenihan的解释是合理的。

精选问答4
题干
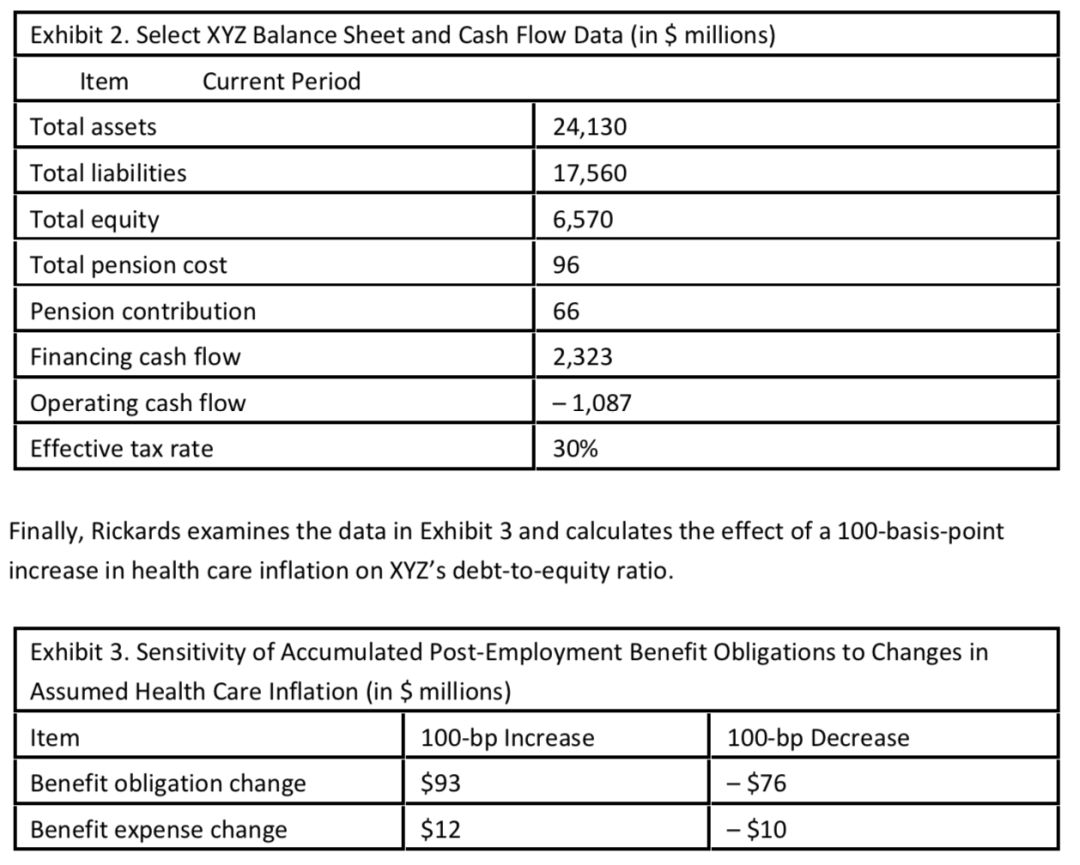
Based on Exhibits 2 and 3, as well as Holmstead’s assumption about future health care inflation, the debt-to-equity ratiocalculated by Rickards for XYZ should be closest to:
A. 2.69.
B. 2.71.
C. 2.73.
答案解析
C is correct.
To calculate the debt-to-equity ratio, both liabilities and total equity need to be adjusted for the estimated impact of a100-bp increase in health care costs. The proposed increase in health care costs will increase total liabilities and decrease equity by the same amount.Consequently, the debt-to-equity ratio changes as follows:
Sensitivity of benefit obligation to 100-bp increase =$93 Adjusted liabilities = $17,560 + $93 = $17,653
Adjusted equity = $6,570 – $93 = $6,477
Adjusted debt-to-equity ratio = $17,653/$6,477 =2.7255
Consequently, a 100-bp increase in health care costsincreases the debt-to-equity ratio to approximately 2.73.
解题思路
原来的liability是17560,原来的equity是6570。如果假设health care inflation变高100个bp,liability会增加93,从资产负债表调平角度看,由于影响plan asset的几项没有需要用到假设的,Health care inflation的改变不会改变asset,那么可以推出equity会相应减少93。计算出Debt-to-equity ratio=(17560+93)/(6570-93)=2.73。
易错点分析
有些同学会问为什么不考虑Benefit expense的改变12,这是因为expense的改变量12其实是包含在93里的。影响PBO的expense有些是确认在I/S中的,有些确认在OCI里,Benefit expense的改变量12是I/S的改变,而equity的改变还受到OCI的影响,所以我们考虑equity变化的时候是用93而不是12。
这是原版书reading 15第33小题,是一个case的其中一问,出题角度很新奇,但其实不难,因为用的就是咱们一级学过的会计恒等式,只要胆大敢做,肯定能做出来。我们可以把这道题的出题角度当做一个特殊案例熟悉一下。

精选问答5
题干
Pedro Ruiz is an analyst for acredit rating agency. One of the companies he follows, Eurexim SA, is based inFrance and complies with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Ruiz has learned that Eurexim used EUR220 million of its own cash and borrowedan equal amount to open a subsidiary in Ukraine. Ukraine is not currently in a hyperinflationary environment, but Ruiz is concerned that this situation couldchange. Ruiz also believes the euro will appreciate against the hryvnia for theforeseeable future.
Given Ruiz’s belief about the direction of exchange rates, Eurexim’sgross profit margin would be highest if it accounts for the Ukraine subsidiary’s inventory using:
A. FIFO and the temporal method.
B. FIFO and the current ratemethod.
C. weighted-average cost and thetemporal method.
答案解析
B iscorrect.
Ruiz expects the EUR to appreciate against the UAH and expects someinflation in the Ukraine. In an inflationary environment, FIFO will generate ahigher gross profit than weighted-average cost.
For either inventory choice,the current rate method will give higher gross profit to the parent company ifthe subsidiary’s currency is depreciating.
Thus, using FIFO and translating using the current rate method will generate a higher gross profit for the parent company, Eurexim SA, than any other combination of choices.
解题思路
gross profit margin=(revenue-COGS)/revenue,因为inventory的计量方法不影响revenue,且temporal method和current rate method转换revenue都是用average rate,区别就在于COGS,因此问哪个选项gross profit margin最大,就相当于问哪个选项的COGS最小。
先明确:FIFO先进先出,COGS反映的是以前购买的存货成本,weighted-average方法下的COGS反映的是加权平均的存货成本。Temporal method使用历史汇率转换COGS,current rate method使用average rate转换COGS。根据题目信息,乌克兰国内物价是在上涨的,乌克兰币相对欧元是在贬值。
A和C选项比,A选项COGS对应的是低价格,高汇率,C选项的COGS反映存货的平均价格,temporal method要追溯历史,所以转换用的汇率是加权平均历史汇率,也就是说C选项对应的是平均价格和平均汇率,很难讲A和C最终算出来的用欧元计价的COGS孰高孰低。但是不管是A和B比,还是C和B比,都是B选项的COGS最小。
A选项的temporal method和B选项的current rate method比,B选项的转换汇率更低,欧元计价的COGS更低。C选项和B选项用的汇率都是平均汇率,但是FIFO和weighted average比较,FIFO下的用乌克兰计价的COGS更低。综上,B选项在inventory计量方法上和转换方法上都能得到更低的COGS。
易错点分析
这是原版书reading 16的第二小题。很多同学在遇到存货计量方法和translation方法放在一起比较的时候就会无从下手,最好是先比较其中一个方法,然后再比较另一个方法,这样思维不容易混乱。temporal method下,COGS用历史汇率转换,是因为B/S上的存货用的是历史汇率,要保持一致性。
有些同学认为,temporal method下用历史汇率转换就等同于用期初的汇率,这也是一个误区,事实上,temporal method下non-monetary资产的转换是要追溯到资产取得时的历史汇率,资产取得的时点不一定就是期初,有可能早于也有可能晚于期初这个时点,对于存货来说,仓库里的存货通常不是一次性采购的,所以有时候题目为了简便,会给一个取得存货时的平均汇率,可以直接拿来用。相应地,COGS的转换汇率也要追溯销售掉的存货的取得时点。

精选问答6
题干
Redline Products, Inc. is a US-based multinational with subsidiaries around the world. One such subsidiary,Acceletron, operates in Singapore. It records inventory using the FIFO method.
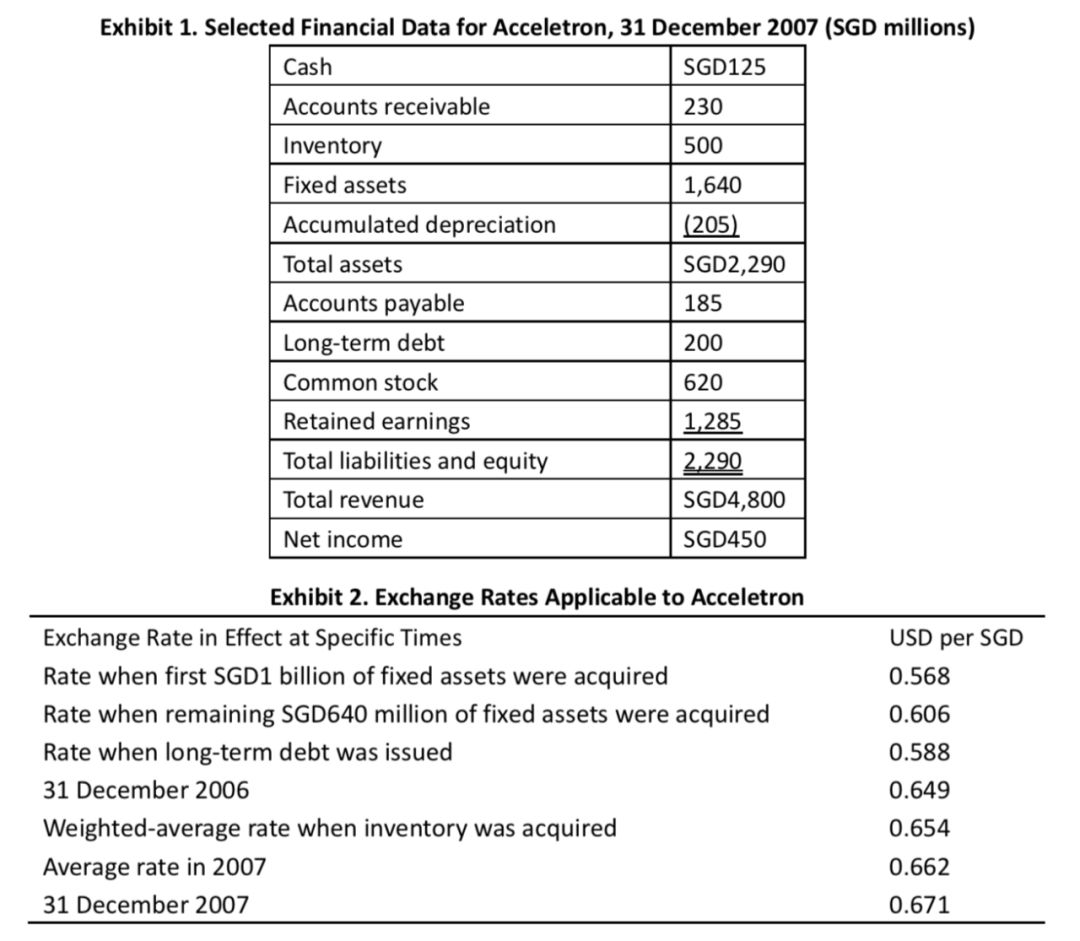
If the US dollar were chosen as the functional currency for Acceletron in 2007, Redline could reduce its balance sheet exposure to exchange rates by:
A. selling SGD30 million of fixed assets for cash.
B. issuing SGD30 million of long-term debt to buy fixed assets.
C. issuing SGD30 million in short-term debt to purchase marketable securities.
答案解析
A is correct.
If the US dollaris the functional currency, the temporal method must be used, and the balance sheet exposure will be the net monetary assets of 125 + 230 – 185 – 200 = –30,or a net monetary liability of SGD30 million.
This net monetary liability would be eliminated if fixed assets (non-monetary) were sold to increase cash. Issuing debt, either short-term or long-term, would increase the net monetary liability.
解题思路
Temporal method下exposure=monetary asset-monetary liability。现在的exposure可以计算一下,是-30。消除exposure,就是要让MA-ML=0,现在是ML比MA多30。
如果要消除exposure,就看看哪个选项的操作能够让MA增加30或者让ML减少30。A选项里fixed asset是non-monetary asset,cash是monetary asset,所以A选项的结果是是MA增加30,ML没变,能够消除exposure。
B选项long-term debt是ML,发债会导致ML增加,MA没变,没法消除exposure。C选项short-term debt也是ML,marketable securities是MA,MA和ML都增加,exposure不变,还是没有消除。所以选A。
易错点分析
有的同学会混淆exposure和translation gain/loss。Exposure是指的面临着汇率变动风险的资产和负债的敞口,不确定性会来来风险,所以才存在exposure。
计算exposure的时候是不考虑汇率变化的,而translation gain/loss是由于exposure带来的,正是因为有资产和负债面临着汇率变动的不确定性,才会在汇率变动的情况下产生gain/loss,non-monetary的资产和负债之所以不会带来exposure,就是因为他们的转换汇率是历史汇率,这个汇率是已经锁定好的,不存在任何的不确定性了。
不管exposure是正还是负,都是有exposure,都有可能带来loss,所以要消除这个敞口,也就是消除公司面临的汇率变动的不确定性,就要让exposure=0。

精选问答7
题干
To evaluate P&C insurancecompanies, Johansson tells Smith that she places emphasis on the efficiency of spending on obtaining new premiums.
The best indicatorof the operations of a P&C insurance company emphasized by Johansson whenevaluating P&C insurance companies is the:
A. combined ratio.
B. underwriting loss ratio.
C. underwriting expense ratio.
答案解析
C is correct.
The underwriting expense ratio is an indicator of the efficiency of money spent on obtaining newpremiums.
The underwriting loss ratio is an indicator of the quality of acompany’s underwriting activities—the degree of success an underwriter has achieved in estimating the risks insured. The combined ratio, a measure of the overall underwriting profitability and efficiency of an underwriting operation,is the sum of these two ratios.
解题思路
Underwriting expense ratio=为了获得新保单而发生的费用/赚到的保费,用来衡量保险公司获得新保单的效率。underwriting lossratio=理赔及理赔相关支出/赚到的保费,衡量的是保险公司估计理赔事件发生的能力,或者说是承保业务的质量。
combined ratio是二者之和,衡量的是保险公司运营的总体效率。根据分析师的描述,我们可以确定分析师所指的ratio就是underwriting expense ratio。
易错点分析
这道题是原版书reading 17课后题第四小题,原版书之前给的答案是combined ratio,今年三月份的时候协会发勘误将答案更正为Underwriting expense ratio。答案后面的英文解析是正确的。
这道题很多人会想当然的选combined ratio,但是combined ratio衡量的是保险公司运营的整体效率,题目很明确的说这个ratio是衡量spending on obtaining new premiums的效率,考的非常直接,就是书上的原文。Reading17这章没有什么计算,理解上也没有难度,有些细节很容易忽略,考试之前一定要再看一看。

精选问答8
题干
Abay is alsoconcerned with earnings quality, so he intends to calculate Bickchip’scash-flow-based accruals ratio and the ratio of operating cash flow beforeinterest and taxes to operating income. To do so, he prepares the informationin Exhibit 3.
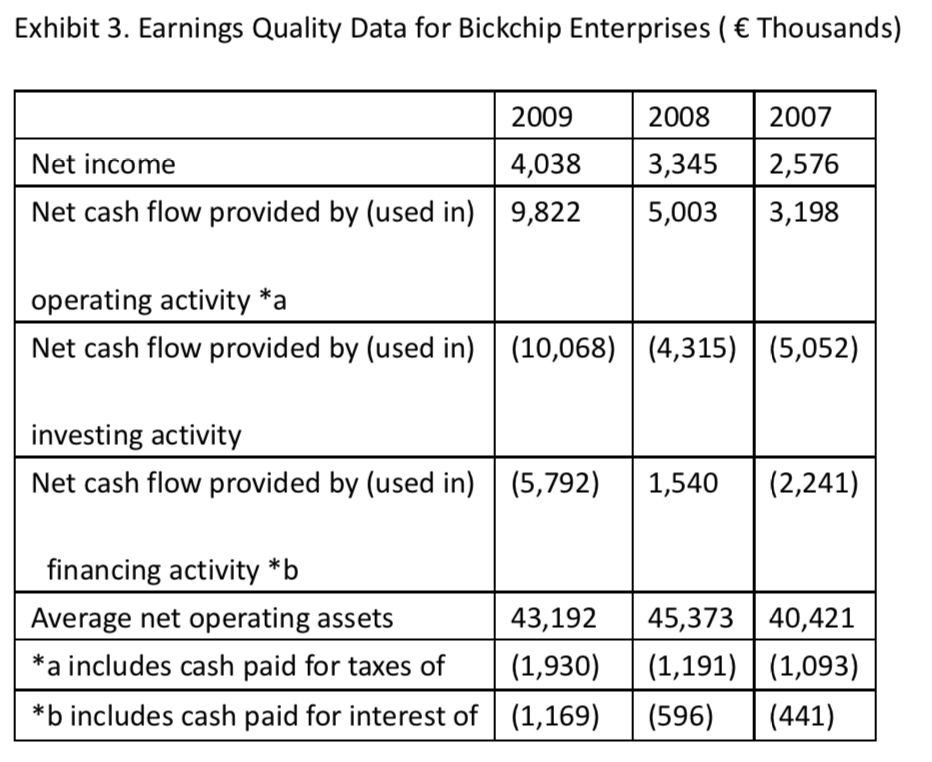
The ratio of operating cash flow beforeinterest and taxes to operating income for Bickchip for 2009 is closest to:
A. 1.6.
B. 1.9.
C. 2.1.
答案解析
B is correct.
Net cash flow provided by (used in) operating activity has to beadjusted for interest and taxes, as necessary, in order to be comparable tooperating income (EBIT).
Bickchip, reporting under IFRS, chose to classifyinterest expense as a financing cash flow so the only necessary adjustment isfor taxes. The operating cash flow before interest and taxes = 9,822 + 1,930 =11,752. Dividing this by EBIT of 6,270 yields 1.9.
解题思路
要求计算的ratio=operating cash flow before interest and taxes/operating income,分子要把CFO中扣除的利息和税加回,但是从Exhibit3最后两行可以知道,Bickchip公司把interest expense归为CFF,把tax归为CFO,因此计算2009年的这个ratio的时候只需要在分子上加回tax,也就是等于(9822+1930)/6270=1.9。
易错点分析
有的同学不理解为什么分子要加回tax和interest,这是为了让分子分母具有可比性而进行的调整,operating income是息税前的利润,还没有扣除interest和tax,但是CFO里面可能是扣掉了这两项的,所以为了分子分母统一,就要把扣掉的这两项加回。
这道题中的CFO只是扣掉了税,那么就只需要把税加回。还有些同学问:CFO里已经“includes”了tax,为什么要再加回,岂不是加了两遍。其实这里的include的意思是“考虑到”,而且题目表格给的CFO是一个net值,必然是扣掉了tax的,从这个角度也应该能理解对。


